Revolutionary 3D Printing Technique Creates Flexible, Functional Circuits
2025-06-25
Author: Li
A Breakthrough in 3D Printing Technology
Researchers from Dalian University of Technology have unveiled an innovative method for 3D printing that is set to disrupt the world of flexible circuits. By employing a tension-driven fluid drawing technique, they've demonstrated the remarkable ability to create functional, flexible circuits.
Redefining Circuit Manufacturing
Dazhi Wang, one of the lead researchers, emphasizes the significance of this development: "Our approach challenges conventional thinking in flexible circuit manufacturing. Instead of extruding ink, we draw it, which gives us unprecedented control over the circuit's structure, speed, and size using only a single needle. This is not merely a new printing method; it fundamentally rethinks how circuits can be constructed in three dimensions. The potential applications in wearable technology and soft robotics are enormous."
How It Works: From Ink to Innovation
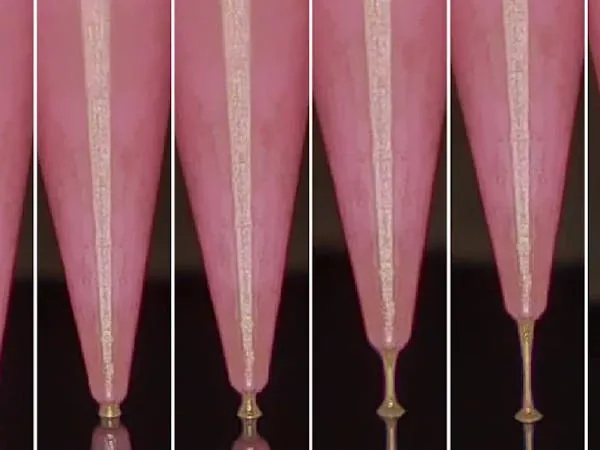
Unlike traditional 3D printing methods that push ink through nozzles, this revolutionary technique draws the conductive ink from a reservoir, similar to sewing with thread. The method utilizes air pressure, ink viscosity, and thermal evaporation to create intricate designs. The ink, composed of silver nanoparticles, is heated to form a connection between the needle and the substrate, then stretched to sculpt 3D structures as thin as 4 micrometers — even thinner than the needle itself!
Flexibility Meets Functionality
Tests revealed that the circuits printed using this method are impressively flexible, enduring 200 bending cycles without any loss of conductivity. To showcase the capabilities of their technique, the research team produced a variety of demonstration circuits. These included addressable LED arrays, heat-sensitive displays visible on thermal cameras, and a flexible self-oscillating multivibrator circuit — all performing exceptionally well.
Future Applications for Wearable Tech and Beyond
The implications of this new manufacturing method are vast. It could revolutionize circuit designs for wearable medical sensors tailored to fit the human body, stretchable displays, and compact Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Moreover, the technique's streamlined process eliminates the need for multiple layers and complex drilling, thereby accelerating production timelines.
The Next Era of Electronics
As this cutting-edge technology emerges, it promises not just to enhance existing applications but to open up new frontiers in the world of electronics, paving the way for a future where flexibility and functionality go hand in hand.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)