Revealing Insights into Epstein–Barr Virus Infection Patterns in Southwestern Saudi Arabia (2020-2023)
2025-08-25
Author: Nur
Unveiling EBV Infection Trends in Southwestern Saudi Arabia
A groundbreaking retrospective study spanning from 2020 to 2023 has unearthed vital information about Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) infections in Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Drawing on electronic health records from a regional laboratory, this research highlights the prevalence and clinical manifestations of EBV among various demographics.
Study Overview: Who Were The Patients?
The study included data from 760 patients who underwent molecular testing for EBV. Out of these, 133 tested positive, giving an overall positivity rate of 17.5%. Each patient’s first positive result was considered to maintain accuracy, enhancing the reliability of the findings.
Diverse Clinical Diagnoses Linked to EBV
The initial diagnoses of EBV-positive patients ranged across nine categories, with infectious diseases being the most prevalent at 28.6%. Hematological disorders followed closely at 20.3%, underscoring significant links between EBV and severe health conditions.
Demographics: A Closer Look
Among the infected, the majority were Saudi nationals (77.4%), reflecting local demographic patterns. Pediatric cases were notably prominent, with 76% of infections occurring in patients under the age of 12. This alarming trend highlights the vulnerability of children to this virus, raising questions about regional healthcare strategies.
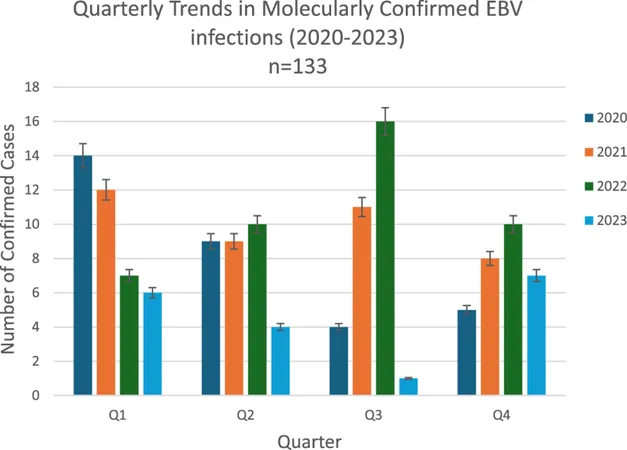
The Yearly Breakdown: Ups and Downs
Analyzing the data revealed fluctuating patterns of EBV infections across the four years. While 2021 and 2022 saw a rise in positive cases, a significant drop occurred in 2023, where only 18 cases were recorded. This sharp decline demands further investigation into what led to this dramatic change.
The Diagnostic Process: High-Tech Solutions
Employing advanced techniques, DNA was extracted from blood samples using cutting-edge technology. The study utilized RT-qPCR tests to ensure accurate detection of EBV DNA, cementing the shift from traditional serological methods to more precise molecular diagnostics.
Potential Causes and Implications of Decreased Cases
The reduction in EBV cases in 2023 could be attributed to a variety of factors, including changes in testing practices post-COVID-19. Previous studies have suggested that COVID-19 may influence EBV reactivation, making it critical to understand the links between these two viruses.
Future Directions: A Call for Enhanced Surveillance
Given the revealing findings of this study, there is an urgent need for improved EBV surveillance, particularly within high-risk populations like children. National-level programs that incorporate both molecular and serological testing will be essential for understanding EBV dynamics, paving the way for informed public health interventions.
Conclusion: A Complex Public Health Challenge
The insights from this study underscore the complexity of EBV infection's role in human health. With its potential to lead to both benign and malignant conditions, raising awareness and enhancing monitoring of EBV is not just important—it’s critical for safeguarding public health in Saudi Arabia.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)