Revealed: The Shocking Link Between Ultra-Processed Foods and Obesity in Tehran!
2025-04-25
Author: Wei
The Global Obesity Epidemic: A Growing Crisis
Obesity has become a worldwide epidemic, with over 1.9 billion adults identified as overweight, including 650 million classified as obese as of 2014. This condition is a major risk factor for serious health issues such as coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and ischemic stroke.
The Rise of Ultra-Processed Foods (UPFs)
The dietary landscape has dramatically shifted over the years, primarily due to the uptake of ultra-processed foods (UPFs). These foods, which constitute around 50% to 60% of daily caloric intake for some, are calorie-dense but nutritionally poor, contributing to escalating obesity rates.
Unmasking the Risks: How UPFs Induce Weight Gain
Studies show that UPFs disrupt metabolic processes, further contributing to weight gain. The NOVA classification categorizes these foods as being primarily derived from industrially altered ingredients rather than whole foods, packed with unhealthy additives but lacking essential nutrients.
Tehran's Growing Concern: A Local Study
A recent study from Tehran aimed to explore the relationship between UPF consumption and various adiposity indexes among adults. It involved 850 participants aged 20 to 59, analyzing how higher UPF intake correlates with indicators of obesity.
Understanding the Study Methods
Participants underwent dietary assessments using a detailed food frequency questionnaire and underwent clinical measurements for various adiposity indexes including BMI, waist circumference, and visceral fat metrics. The research employed advanced statistical methods to refine its findings.
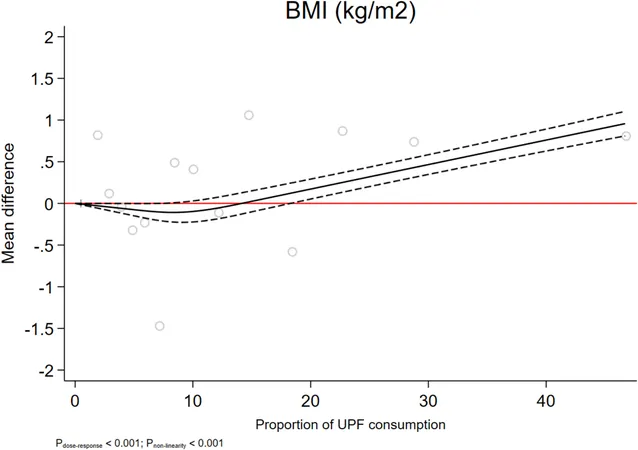
Startling Findings: UPFs and Weight Gain Correlation
The data revealed unsettling insights: increased UPF consumption correlated with higher BMI and various adiposity measurements. Although some associations like the waist-to-hip ratio remained unclear, the evidence pointing towards UPFs exacerbating obesity remains compelling.
Cross-National Insights: A Shared Struggle
These findings align with international studies that show similar patterns of association between UPF consumption and rising obesity rates in other parts of the world. Individuals consuming higher quantities of UPFs not only face weight challenges but also risk metabolic disturbances.
What’s Next? Understanding the Underlying Mechanisms
The mechanisms driving these associations include high caloric density, added sugars, and unhealthy fats in UPFs, which not only promote excess calorie intake but also disrupt hunger hormones, leading to increased cravings and overeating.
Strength and Limitations of the Study
While this Tehran study robustly assessed several adiposity-related metrics and employed sophisticated analytical methods to validate findings, it still faced limitations such as potential reporting biases and the inability to establish causal relationships due to its cross-sectional design.
The Bottom Line: A Call to Action
As the evidence mounts, it’s crucial to address the rising consumption of UPFs to combat obesity effectively. Public health initiatives should promote awareness about the health risks associated with these foods and encourage healthier dietary practices.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)