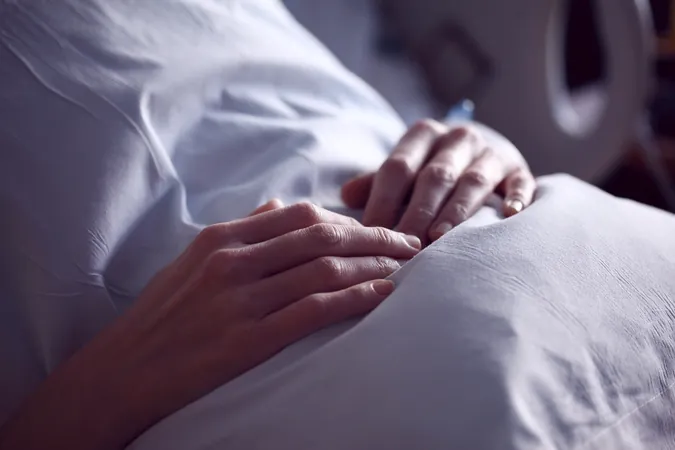

Revealed: Gabapentinoids Show No Direct Link to Self-Harm Risk, But Monitoring is Key!
2025-04-30
Author: Yu
Groundbreaking Study Spotlights Gabapentinoids and Self-Harm Risks
A recent UK study published in The BMJ has thrown light on an important aspect of mental health treatment: the use of gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin. Surprisingly, researchers found that these medications are not directly linked to an increased risk of self-harm.
Understanding Gabapentinoids: The Dual Nature of Risk
Gabapentinoids are commonly prescribed for conditions like epilepsy, nerve pain, and anxiety disorders. While previous studies raised concerns about these drugs potentially increasing self-harm risk, this investigation sheds new light on timing, revealing that the risk appears to be higher before and shortly after treatment.
Diving Deep into the Data
Over a span of two decades, researchers analyzed the electronic health records of over 10,000 adults who were prescribed gabapentinoids and had a history of self-harm. By examining different timeframes—90 days prior to treatment, during treatment, and 14 days after stopping therapy—they aimed to clarify the complex relationship between these drugs and self-harm.
Key Findings: The Timing of Self-Harm Risks
The results are eye-opening: self-harm rates surged by a staggering 69% in the 90 days before starting treatment. During the actual treatment phase, this risk decreased significantly, but alarmingly spiked to nearly 30 per 100 person years in the two weeks following cessation of the medication. This indicates that while gabapentinoids may not cause self-harm, those at risk often seek these treatments.
Cautions and Considerations
The researchers stress the need for careful patient monitoring during and after gabapentinoid treatment, noting that their findings, although robust, are observational in nature and may not capture all cases of self-harm.
The Need for Continued Research
While this study provides invaluable insights, it highlights the necessity for further research across diverse populations. It opens the door to questions about additional supervision needed for young adults and individuals without psychiatric diagnoses who are prescribed these medications.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Monitoring
As the landscape of mental health treatment continues to evolve, this investigation underscores the critical importance of ongoing support and monitoring of individuals on gabapentinoids, particularly during the vulnerable periods surrounding their treatment.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)