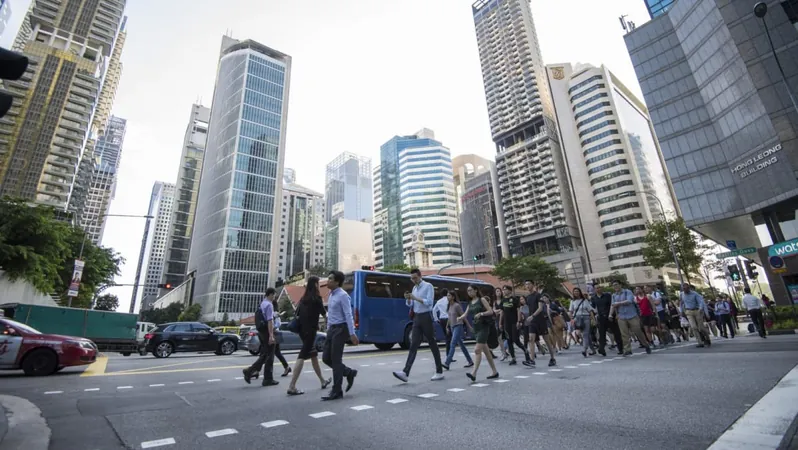

Retrenchments Decrease in Singapore for 2024: What This Means for the Employment Landscape
2025-01-27
Author: Arjun
SINGAPORE: In a promising sign for the economy, the Ministry of Manpower (MOM) has revealed that the number of retrenchments in Singapore fell in 2024, showing a decline to 12,930 from the previous year’s 14,590. This trend indicates that businesses are stabilizing, although employment growth has begun to slow down, raising questions about the future workforce landscape.
The retrenchment rate per 1,000 employees also saw an improvement, decreasing from 6.7 in 2023 to 5.8 this year, which puts the current statistics well within the non-recession norms. However, the last quarter of 2024 raised some concerns, as layoffs surged to 3,600 compared to 3,050 in the third quarter.
The MOM reported that the primary reason for retrenchments was business reorganization and restructuring, which emphasizes a shift in how companies are operating in response to evolving market demands. Layoffs were notably higher in the manufacturing and services sectors, while the construction sector remained relatively stable.
Unemployment Rates: A Stable Yet Cautionary Tale
While unemployment rates seem to hold steady, the annual unemployment rate edged up slightly from 1.9% in 2023 to 2%. The resident unemployment rate rose from 2.7% to 2.8%, with citizen unemployment holding steady at 2.9%. Interestingly, there was an increase in unemployment rates from September to October 2024, suggesting that seasonal trends may have an impact on job availability. However, these rates remained within the normal range for non-recession periods.
Employment Growth: Slowing but Steady
Despite the slowing pace, total employment in Singapore continued to grow in 2024, with an anticipated increase of 45,500 jobs, significantly less than the 78,800 in 2023, indicating a gradual cooling of the job market. Good news came from the resident employment sector, which grew after a previous decline, primarily in high-skilled fields such as professional services, financial services, and health and social services.
However, non-resident employment growth slowed, even as hiring in construction remained robust. Key sectors, notably professional services, financial services, and health and social services, continued to see a demand for qualified residents, even with a seasonal uptick in retail trade due to year-end hiring.
Outlook: The Future of Singapore's Labour Market
Looking ahead, the outlook for Singapore's labour market remains cautiously optimistic. Polls conducted by MOM indicated a rise in the number of companies planning to hire more workers, jumping from 43% in September to 46% in December. Additionally, those planning to increase wages doubled from 16% to 32% during the same period.
Nonetheless, with ongoing uncertainties in the global economy, both employers and workers face challenges that necessitate continuous adaptation and upskilling. The MOM highlighted the importance of recognizing the aging workforce as a long-term issue and the need for transformative strategies to maintain and enhance productivity.
To secure Singapore's economic competitiveness and effectively utilize the local talent pool, the ministry underscored the necessity of leveraging foreign investments and global talent. This approach is expected to create more opportunities for local businesses and high-quality employment for Singaporeans.
The dynamics of the job market in Singapore point towards a necessary evolution, and both employees and employers must remain agile in navigating these changes to achieve long-term growth and stability.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)