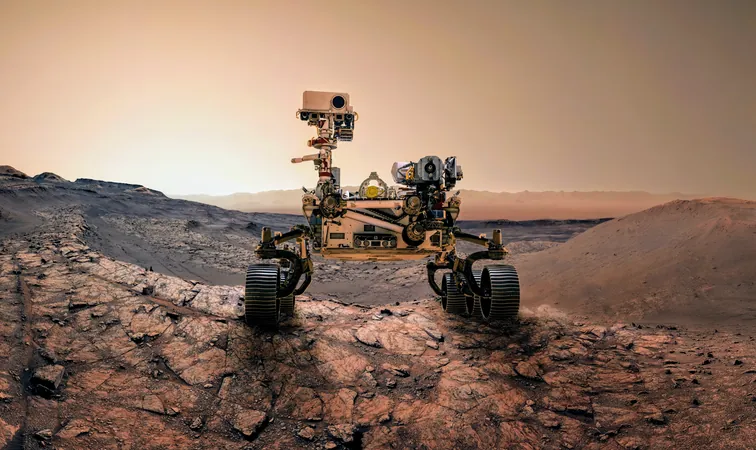

Perseverance Rover Triumphs as It Conquers Jezero Crater's Lookout Hill
2024-12-25
Author: Daniel
NASA's Perseverance rover achieves a major milestone
NASA's Perseverance rover has achieved a major milestone in its mission on the Martian surface by successfully ascending "Lookout Hill," the highest point of the Jezero Crater’s rim. This climb marks the end of an arduous journey filled with challenges and triumphs, as the rover navigated a steep incline of 20 percent, ultimately traversing 1,640 vertical feet (500 meters) over the course of three months.
During its ascent, the rover collected valuable geological observations, enhancing our understanding of Martian landscapes. "The journey to Lookout Hill was fraught with obstacles, but our team operated with incredible skill and ingenuity," said Steven Lee, the deputy project manager for Perseverance, during a recent media briefing at the American Geophysical Union's annual meeting.
Innovative strategies were employed along the way, including the decision to maneuver backwards when faced with particularly tough terrain. "This mission showcases Perseverance's resilience and adaptability," Lee affirmed, highlighting the rover's engineering prowess.
A New Phase of Exploration: The Northern Rim Campaign
Despite the accomplishment at Lookout Hill, Perseverance’s mission is far from over. The rover is now entering its fifth phase, dubbed the "Northern Rim" campaign. It aims to explore up to four geological areas of intrigue, gather crucial samples, and cover approximately four miles (6.4 kilometers). “This phase will lead us into new geological terrains, offering profound scientific opportunities,” stated Ken Farley, project scientist for Perseverance.
The Northern Rim campaign represents a major shift in focus, moving from rocks that partially formed during the craters' inception to rocks that were ejected from deep beneath the Martian surface due to historical impacts. These ancient materials could provide insights into Mars's early geological history, which parallels our understanding of Earth’s formative years.
Exploring Ancient Martian History
One of the first geological features Perseverance will investigate in this new phase is "Witch Hazel Hill." Each layered outcrop there is seen as a chapter in the story of Mars, according to scientist Candice Bedford. As the rover moves downward, it will uncover deeper records of the planet’s past environments.
Following Witch Hazel Hill, Perseverance plans to travel to "Lac de Charmes," located roughly two miles south. This terrain is thought to be less impacted by Jezero Crater’s formation, providing a unique vantage point for studying Martian geology. Additionally, the rover will investigate large blocks known as megabreccia, which may reveal remnants of the ancient bedrock altered by cataclysmic impacts.
The Pursuit of Astrobiology and Future Exploration
At the heart of Perseverance’s mission is the quest for signs of ancient life, particularly microbial organisms. The rover’s geological analysis plays a critical role in preparing for future human missions to Mars. An integral part of NASA's broader Moon to Mars exploration strategy, the Mars 2020 Perseverance mission collaborates with the European Space Agency on the ambitious Mars Sample Return Program. This initiative aims to retrieve sealed samples from Mars and bring them back to Earth for comprehensive examination.
Controlled by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Perseverance’s operations demonstrate humanity's unwavering curiosity and commitment to understanding life beyond our planet. As the rover continues to unveil the mysteries of Mars, each discovery brings us closer to answering fundamental questions about our own existence.
For those eager to follow Perseverance's journey and the groundbreaking discoveries to come, be sure to stay updated as we uncover the secrets of the Red Planet!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)