New Study Reveals Serotonin's Surprising Role in Brain's Reward Processing
2025-04-04
Author: Jia
New Study Reveals Serotonin's Surprising Role in Brain's Reward Processing
In our fast-paced lives, we constantly face a myriad of decisions—ranging from everyday choices to long-term aspirations. But have you ever wondered how our brain processes these decisions and the role the neurotransmitter serotonin plays in this intricate dance? A groundbreaking study from an interdisciplinary team at the University of Ottawa has uncovered fascinating insights that shed light on the mysterious functions of serotonin within the brain’s reward processing system.
Published in the prestigious journal *Nature*, this significant research collaboration offers profound implications across neuroscience, psychology, and psychiatry, enhancing our understanding of serotonin not only in mood regulation but also in learning and motivational behavior.
Serotonin: More Than Just the "Pleasure Chemical"
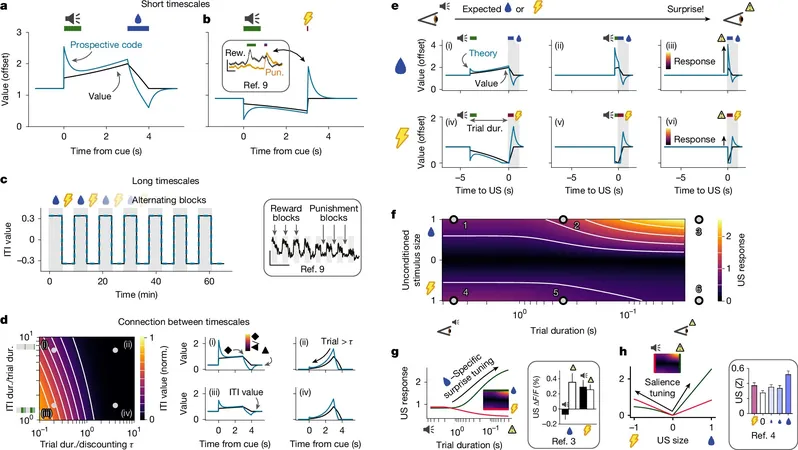
Commonly referred to as the brain's "pleasure chemical," serotonin's true role in the nervous system has remained enigmatic. This neurotransmitter influences various functions, including mood, movement, appetite, and sleep-wake cycles. The mystery deepens as serotonin is activated by experiences of pleasure, pain, and surprise alike, leading researchers to seek a more comprehensive understanding of its implications.
The groundbreaking study proposes a novel perspective on serotonin as a "prospective code for value." This concept serves as a biological blueprint for how our brain evaluates potential future rewards. Interestingly, it explains why serotonin neurons activate in response to both rewards and punishments—especially when the rewards are unexpected.
According to Dr. Richard Naud, a key author of the study, "Our work addresses an essential question: What does serotonin communicate to the brain? Our findings indicate that its messages align closely with expectations for future rewards."
Dr. Jean-Claude Béïque, another co-author, elaborates: "Your brain continuously evaluates the expected value of different actions as you navigate a constantly changing environment. This is no easy task. We propose that serotonin encodes the expected value of various environments and choices, ultimately guiding everyday decisions."
The Genesis of the Research
This innovative research journey began several years ago when Emerson Harkin, a Ph.D. student in Dr. Naud's lab, started simulating reinforcement-learning models while examining the biophysical properties of serotonin neurons. Harkin and his team were among the first to explore the idea that serotonin neurons could be triggered by alterations in the surroundings, such as the anticipation of a reward or the cessation of a punishment—inspired by experimental work with mouse models.
The researchers noted a significant shift in their understanding: prior results, which had once been perplexing or contradictory, began to coalesce around this new perspective.
The Road Ahead
As the research team looks to the future, their focus narrows on investigating how serotonin affects behavior and figuring out how other parts of the brain interpret serotonin's messages. Dr. Naud emphasizes a hopeful avenue: leveraging the principles of reinforcement learning could provide a valuable framework for these further studies.
This study not only enriches our understanding of serotonin's multifaceted role but also opens the door to potential therapeutic approaches for conditions influenced by serotonin, such as depression and anxiety. Stay tuned—this could be a pivotal breakthrough in neuroscience that might redefine our perception of mental health and decision-making in the brain!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)