
New NASA Research Unveils Groundbreaking Insights into Space Life Sciences
2025-01-27
Author: Li
New NASA Research Unveils Groundbreaking Insights into Space Life Sciences
On January 24, 2025, NASA released its latest findings centered on space life science research, highlighting innovative studies that explore the profound impacts of space flight on biological systems. Here’s a closer look at some noteworthy research pieces and their implications for future long-duration space missions.
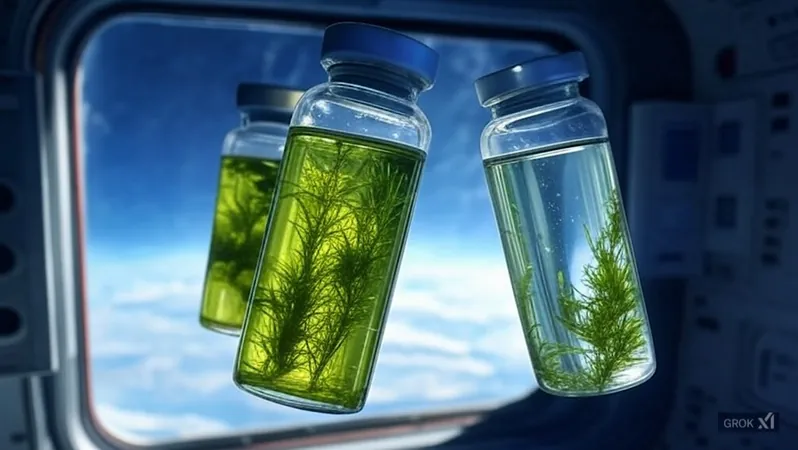
1. Seeds in Space: How Microgravity Affects Plant Growth
A pivotal study conducted by Richards et al. examines seeds subjected to simulated deep space environments. Utilizing the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) flight facility, the team found that microgravity alters the growth patterns of seeds, potentially reshaping our understanding of agricultural practices in space. This project, supported by the NASA Biological and Physical Sciences Division, indicates exciting possibilities for sustaining food production during extended space missions.
2. Cosmic Rays and Mouse Lungs: Long-term Health Effects
Chancellor et al. focused on the long-term impacts of microgravity and galactic cosmic radiation on mouse lung health. This research revealed sex-specific epigenetic changes, suggesting that living in space could pose unique health challenges that need more robust strategies to mitigate risks for astronauts. Such findings are crucial for the planning of future missions, particularly to Mars.
3. Enhancing Anomaly Resolution with Virtual Assistants
In a groundbreaking exploration of human-computer interaction, Josan et al. investigated how a virtual assistant, named Daphne-AT, can boost crew performance during spacecraft anomalies. The study highlighted that the use of virtual assistants can significantly enhance situational awareness and reduce mental workload—key factors in time-critical environments. As space missions become more complex, such technologies could be vital for astronaut safety and efficiency.
4. Machine Learning in Space Research
Casaletto and colleagues introduced a novel approach to analyzing gene expression correlated with space-flown mice using the Causal Research and Inference Search Platform (CRISP). This innovative method bridges machine learning with biological research, offering new perspectives on how space travel affects genetic expression and potentially influencing future biomedical developments.
5. Understanding Behavioral Health for Long Missions
In a focused effort on mental health, Shepanek's investigation into behavioral health challenges highlights the importance of psychological well-being during long missions. As NASA prepares for future explorations, such as potential missions to Mars, attention to mental health will be pivotal in ensuring astronaut wellbeing.
6. Cerebral Blood Flow and Posture Adaptation Studies
New insights into human physiology in space were presented by Possnig et al. Their work revealed how cerebral blood flow is affected by different postures in microgravity, which is essential information for optimizing astronaut health and operational efficiency during missions involving prolonged low-gravity conditions.
Implications for Future Missions
The broad array of studies released by NASA underscores the agency's commitment to understanding and addressing the potential challenges posed by long-duration space missions. As preparations continue for missions to the Moon and Mars, these insights are not just academic; they pave the way for practical solutions to enhance astronaut health, safety, and performance in the unforgiving environment of outer space.
With research efforts like these, humanity stands on the brink of remarkable advancements in space exploration, making it imperative to keep a pulse on NASA's ongoing projects. As we strive to become a multi-planetary species, understanding the complexities of life beyond Earth has never been more crucial.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)