New Hope in the Fight Against Obesity: Targeting Proteins Known as Prohibitins!
2024-09-24
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University have unveiled the critical role of proteins called prohibitins in obesity and inflammation, potentially opening the door for new therapeutic strategies.
Global Obesity Crisis
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 43% of adults worldwide were reported to be overweight in 2022, with 16% classified as obese. This global crisis is not just about appearances; overweight individuals face severe health repercussions, including strain on the cardiovascular, respiratory, and locomotor systems. Furthermore, obesity triggers significant molecular changes within cells, activating genes responsible for aging, cell death, and inflammation.
Role of Prohibitins
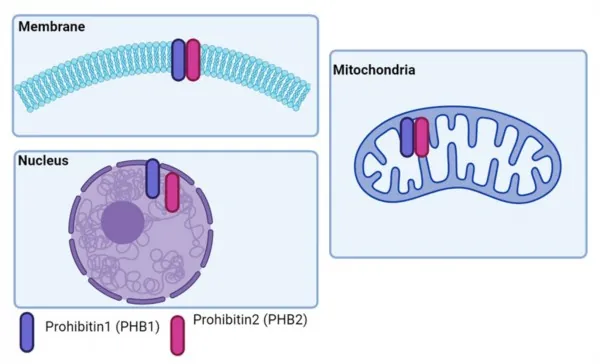
Research highlights that prohibitins play a vital role in maintaining the balance of many intracellular processes, including cell division and mitochondrial function. However, until now, information about their involvement in inflammatory responses associated with obesity was limited, preventing them from being considered potential therapeutic targets.
Research Findings
The team from Kaliningrad, in collaboration with scientists from Siberian State Medical University, conducted a thorough analysis of existing literature on prohibitins. Their findings revealed that these proteins are present on the membranes of various immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages. They work in concert with membrane receptors, releasing anti-inflammatory substances that help combat tissue inflammation resulting from lipid overload in fat cells.
Mechanisms of Action
Interestingly, prohibitins are also located within mitochondria, where they monitor mitochondrial DNA quality and oversee the elimination of damaged mitochondria due to oxidative stress. They facilitate the transfer of short DNA fragments from damaged mitochondria to the cytoplasm, instigating an inflammatory reaction. Simultaneously, prohibitins ensure that healthy mitochondria do not divide uncontrollably, thus maintaining cellular health.
Abnormal Prohibitins and Cell Division
Moreover, exceed expectations, prohibitins are found within the nucleus of the cell, where an abnormal buildup of these proteins has been linked to disrupted cell division and cell-cycle arrest.
Promising Compounds
Perhaps most excitingly, the researchers discovered promising low-molecular weight compounds that manipulate prohibitins' activity, leading to the breakdown of fat cells and enhanced glucose utilization. Some studies have also reported the anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor properties of these small molecules, including flavoglins and the bacterial polysaccharide Vi.
Conclusion
Natalia Todosenko, a lead researcher from the Center of Immunology and Cell Biotechnology at Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University, stated, "Our analysis demonstrates that prohibitins can serve as potential molecular targets for obesity treatments. However, their diverse actions in different tissues require further investigation. Understanding prohibitins' roles in metabolic syndrome and obesity will allow us to develop more targeted and effective treatments. We aim to continue our research in this field, focusing specifically on the mechanisms within blood cells, fat cells, and liver cells under both normal and pathological conditions."
Future Outlook
As obesity continues to pose serious health risks globally, this research shines a light on novel strategies to combat this epidemic. Could targeting prohibitins be the key to unlocking new treatments? Stay tuned for updates on this exciting frontier in obesity research!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)