New Discoveries Unveil the Crucial Role of NAD in Aging and Disease - What You Need to Know!
2024-12-23
Author: Mei
Introduction
Researchers from the University of Bergen (UiB) have uncovered game-changing insights into the role of a vital molecule—NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)—in the aging process and its connection to various diseases. Their groundbreaking study, published in Nature Metabolism, reveals how disrupted NAD levels may contribute to neurodegenerative disorders and other health issues.
Significance of NAD
Leading this pivotal research, Professor Mathias Ziegler emphasizes the molecule's significance: “NAD is fundamental to life, integral to all cellular processes. When NAD levels are dysregulated, it influences aging and a host of conditions ranging from cancer to diabetes and neurodegeneration.”
NAD: The Cell’s Rechargeable Battery
At the heart of every bodily function is energy. This energy is derived from the nutrients we consume and is converted into a form our cells can utilize. Professor Ziegler explains, “NAD functions like a rechargeable battery in these processes, storing energy from food to fuel cellular activities, particularly in the mitochondria—the cell’s powerhouse.
NAD also plays a crucial role beyond energy metabolism; it is a signaling molecule that regulates fundamental cellular functions, including gene expression and DNA repair. However, as we age, DNA damage accumulates, leading to an increased demand for NAD, which tends to decline over the years. This depletion is a concern, particularly when mitochondrial health is compromised.
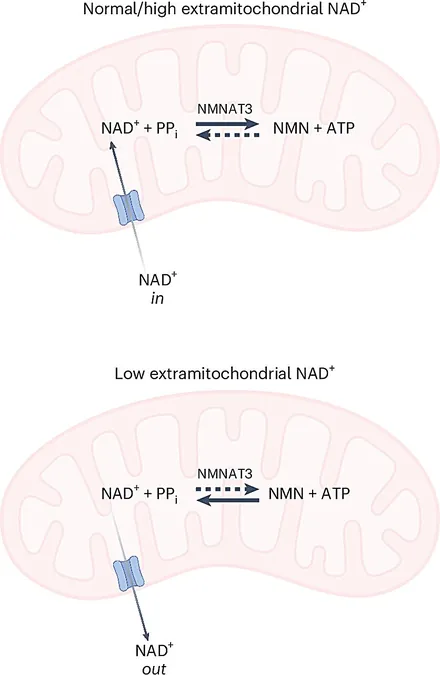
Crucial Insights from Advanced Research
To delve deeper into the cellular responses to reduced NAD levels, Ziegler’s team employed creative models and advanced technologies, including high-resolution mass spectrometry, to assess how cells cope as NAD wanes with age. In a surprising twist, they uncovered that mitochondria act as a reservoir for NAD, replenishing it during times of heightened demand.
Ph.D. student Lena Høyland notes, “The findings indicate that while decreases in cellular NAD are generally manageable, lasting issues with mitochondrial function can prevent adequate NAD supply, potentially impacting vital energy-dependent processes.”
The Impact of Mitochondrial Dysfunction on Health
Recent research has increasingly linked mitochondrial dysfunction and lowered NAD levels to age-related conditions such as dementia and neurodegenerative diseases. Alarmingly, chronic depletion of mitochondrial NAD could be a key driver of these aging-related disorders.
Promisingly, initial clinical trials in Norway and beyond, focusing on NAD supplementation, have yielded optimistic results. These therapies aim to boost NAD levels in individuals experiencing age-related conditions.
A Step Toward Future Solutions
As a result of this pioneering study, researchers express excitement over uncovering additional mechanisms that may influence disease development and progression. “Our work underscores the essential nature of foundational research in identifying possible targets for diminishing the effects of aging and treating age-associated diseases,” states Professor Ziegler.
In light of new insights into NAD’s critical roles, the scientific community is poised to explore therapeutic avenues that may revolutionize how we approach aging and disease management. Stay tuned, as this exciting research could change the landscape of healthcare as we know it!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)