Neurons: The Brain's Rhythm Kings of Thought and Memory!
2025-06-16
Author: Jia
Unlocking the Brain's Mysteries
Imagine your brain as a sophisticated GPS, ceaselessly mapping the world around you, often without your awareness. This remarkable functionality stems from minuscule electrical signals pinging between neurons—your brain's specialized cells critical for thinking, movement, memory, and emotions. These signals dance to rhythmic beats, like slower theta waves and faster gamma waves, orchestrating how your brain processes information.
A Groundbreaking Discovery
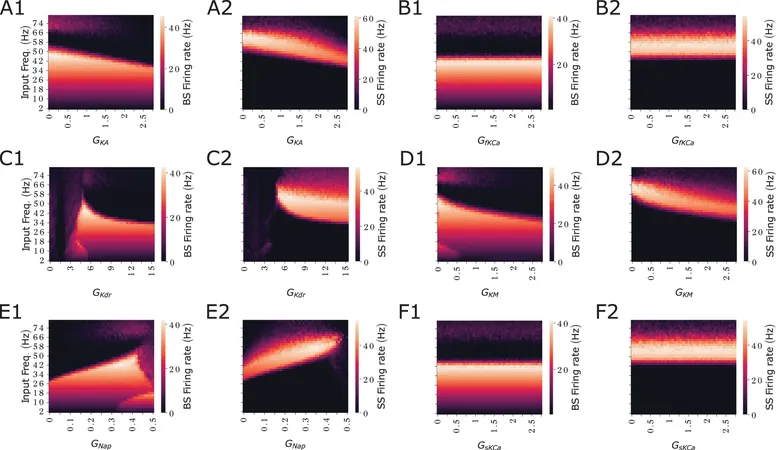
A recent study from Florida Atlantic University, in collaboration with Erasmus Medical Center and the University of Amsterdam, has revealed an astonishing ability of hippocampal neurons to simultaneously process information using multiple brain rhythms. This research, featured in PLOS Computational Biology, uncovers how individual neurons can toggle between firing isolated spikes and rapid bursts, a phenomenon the team has dubbed "interleaved resonance."
Implications for Memory and Learning
This discovery illuminates how our brains seamlessly organize thoughts related to navigation and memory, with significant implications for neurological disorders like epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, and schizophrenia. The focus was on CA1 pyramidal neurons, which play a pivotal role in memory formation and spatial navigation—the very essence of knowing where we are and how to get there.
How Neurons Adapt to Rhythm Changes
Using cutting-edge voltage imaging and advanced computational models, researchers demonstrated that these neurons can respond to both theta and gamma inputs simultaneously—but with distinct reactions. This results in “double coding,” where bursts resonate with theta waves while single spikes align with gamma waves, enabling neurons to convey complex information in real-time.
An Amazing Flexibility!
Senior author Rodrigo Pena, Ph.D., likens this neuron behavior to a multi-band radio, adjusting to different frequencies as needed. He emphasizes the newfound flexibility and incredible power of this system, suggesting it could revolutionize our understanding of brain functions and disorders.
How Internal Settings Influence Behavior
Interestingly, the study reveals that the neurons' internal settings—specifically three ion-driven currents—play a crucial role in this adaptive behavior. By altering these internal factors, neurons can switch their resonance preferences and firing patterns, giving them the unique ability to encode information fluidly based on timing and context.
A New Way to Understand Brain Functions
This "double coding" phenomenon heralds a new chapter in neuroscience, showing that neurons are not rigid but can dynamically alter their responses based on external stimuli and their internal state. Imagine a single neuron not being confined to one signal type but capable of transmitting multiple layers of information according to what’s happening at any given moment!
The Future of Treatment for Neurological Disorders
Pena believes understanding these mechanisms can guide future treatments aimed at restoring normal neuronal function in cases where it’s disrupted. With the brain's building blocks proving to be more dynamic than previously thought, this research holds promise for transformative advances in how we comprehend and address neurological challenges.
The Journey Ahead
As we unravel the complexities of brain rhythms and neuronal behavior, each revelation brings us one step closer to unlocking the mysteries of memory formation and cognitive processing. This exciting study not only enhances our understanding of brain dynamics but also opens up new avenues for addressing conditions that disrupt these vital processes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)