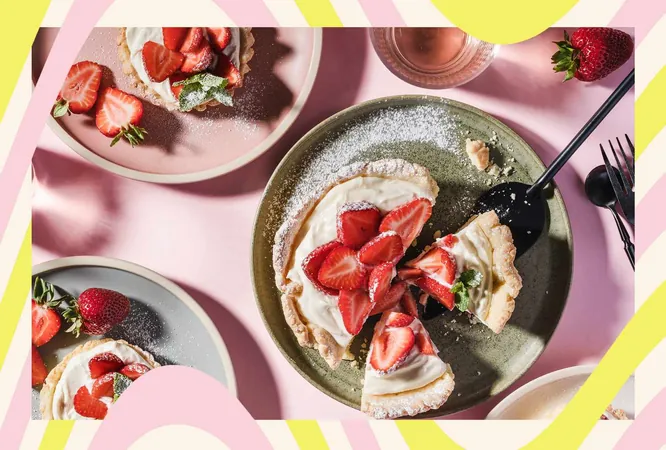

Natural vs. Added Sugars: You Won't Believe How They Differ!
2025-03-11
Author: Ming
Understanding Added Sugars
So, what exactly are added sugars? According to nutrition expert Claire Chewning, RD, added sugars are those that are incorporated into food products during processing or preparation. These sugars go by many names, including: - Agave nectar - Brown sugar - Cane sugar - High-fructose corn syrup - Fruit juice concentrates - Honey - Molasses - Maple syrup Why are these sugars added? They enhance flavor, improve texture, and even act as preservatives to extend shelf life. You'll commonly find added sugars lurking in sweetened yogurts, breakfast cereals, sodas, desserts, and various condiments such as ketchup and barbecue sauce.
The Sweet Side of Natural Sugars
Natural sugars, on the other hand, are those found inherently in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy. Unlike added sugars, these sources provide vital nutrients alongside their sugars. For example, fruits are not only sweet but also rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber that help maintain balanced blood sugar levels and provide satiety.
Health Implications: Added vs. Natural
Believe it or not, the types of sugars you consume can have drastically different effects on your body! Here's what Chewning emphasizes: - **Whole foods vs. Processed:** Foods containing natural sugars, like fresh fruits and vegetables, contribute to overall health. Regularly consuming these can lower the risk of numerous chronic diseases, including heart disease and certain cancers. In fact, a significant meta-analysis revealed that about five servings of fruits and vegetables per day greatly reduces mortality risk. - **The Role of Added Sugars:** While natural sugars integrate seamlessly into a nutritious diet, excessive consumption of added sugars can lead to various health issues. Rapid spikes in blood sugar from sugary snacks can leave you feeling hungry shortly after, leading to overeating. This behavior can pave the way for conditions such as weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and even tooth decay.
Tips to Tame Your Sweet Tooth
Most adults consume about 17 teaspoons of added sugars daily—well above the recommended limit. Here are some strategies to help cut back: 1. **Set a Sugar Goal:** The Dietary Guidelines for Americans suggest keeping added sugars to less than 10% of total daily caloric intake. If your intake is 2,000 calories a day, that's about 12 teaspoons of added sugar, which helps you evaluate your consumption. 2. **Read Nutrition Labels:** Familiarize yourself with the "Total Sugars" and "Added Sugars" sections on nutrition labels. A good benchmark is to aim for 5% or less of the Daily Value for added sugars per serving. 3. **Focus on Balanced Meals:** Ensure your meals consist of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and fiber. This balance helps manage cravings and minimize the temptation of sweet snacks. 4. **Be Mindful of Beverages:** Sugary drinks are major culprits of added sugar intake. Opt for unsweetened beverages like sparkling water, or gradually reduce sugary coffee or tea syrups to ease your palate. 5. **Savor Your Sweet Treats:** Allowing yourself to enjoy desserts in moderation can take away the urge to binge later. Approach each dessert with mindfulness, appreciating the taste without guilt.
The Final Scoop
Understanding the differences between natural and added sugars can empower you to make better dietary choices. By focusing on whole foods and minimizing added sugars, you’ll not only enhance your health and vitality but also enjoy your meals guilt-free. Remember, moderation is key, and every food can have its rightful place in your diet!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)