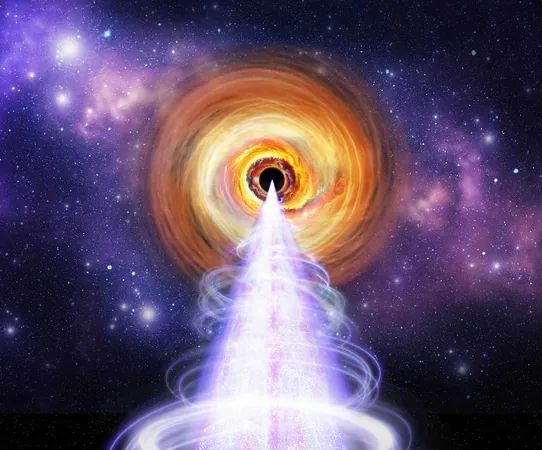

NASA's IXPE Unlocks Secrets of X-Ray Emissions from Mysterious Blazar
2025-05-08
Author: Wei Ling
Blazar BL Lacertae: The Cosmic Puzzle Revealed
A breakthrough in space science has illuminated the enigmatic blazar BL Lacertae, revealing the source of its powerful X-ray emissions. This achievement stems from groundbreaking research utilizing NASA's Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE). Situated directly in our line of sight, BL Lacertae is a supermassive black hole emitting jets that provide an extraordinary opportunity for astrophysical study.
The Dance of Matter and Energy
Surrounded by a mesmerizing halo, BL Lacertae features a bright accretion disk where swirling material spirals ominously toward the black hole's event horizon. As matter is drawn in, it simultaneously ejects high-speed jets of electrons propelled by helical magnetic fields. This dual-action creates a dynamic environment ripe for understanding the mysteries of X-ray generation.
From Variable Star to Astrophysical Marvel
Initially misclassified as a variable star upon its discovery in 1929, BL Lacertae was later recognized as one of the universe's first blazars. These remarkable cosmic bodies are characterized by a galaxy core shooting out jets of ionized matter at nearly light speed—a term that has become essential in astrophysics since its introduction in 1978.
Decoding the X-Ray Enigma
Before this latest research, scientists were divided over the genesis of BL Lacertae's X-rays. Competing theories suggested either proton interactions with photons or electron-photon interactions as the culprits. This dilemma was addressed by measuring X-ray polarization, with IXPE uniquely capable of capturing the required data.
Lead researcher Iván Agudo from Spain's Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía stated, "This was one of the biggest mysteries surrounding supermassive black hole jets, and IXPE has finally equipped us to unveil it." The study involved seven days of intensive observation, culminating in valuable insights.
The Electron Hypothesis Confirmed
Analyzing IXPE data, researchers provided robust evidence aligning with the electron-photon interaction theory through observations of Compton scattering. This phenomenon occurs when photons transfer energy to electrons, significantly impacting their wavelengths. Notably, during the study, BL Lacertae exhibited a high optical polarization of 47.5%, while X-rays showed less than 7.6% polarization—crucial indicators that suggested electrons were indeed responsible for the X-ray emissions.
Co-author Ioannis Liodakis celebrated the findings, noting, "This is not only the most polarized BL Lac has been in 30 years, but it also represents the highest polarization any blazar has ever recorded!"
IXPE: A Glimpse into the Future
Launched in 2021, IXPE is a collaborative effort between NASA and the Italian Space Agency with contributions from various countries. As it continues its mission to explore the polarization of X-rays emitted from diverse cosmic phenomena, the spacecraft has over a year and a half of operations left.
Enrico Costa, an astrophysicist involved in the project, remarked, "IXPE has tackled another black hole mystery. Its polarized X-ray vision has solved several long-standing puzzles, and this discovery is monumental." As blazars are ever-changing and full of surprises, the team aims to uncover even more of these cosmic wonders.
Stay Tuned for More Astrophysical Breakthroughs!
The research paper titled "High Optical to X-ray Polarization Ratio Reveals Compton Scattering in BL Lacertae’s Jet" is set to be published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, promising to keep the scientific community abuzz with ongoing discoveries.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)