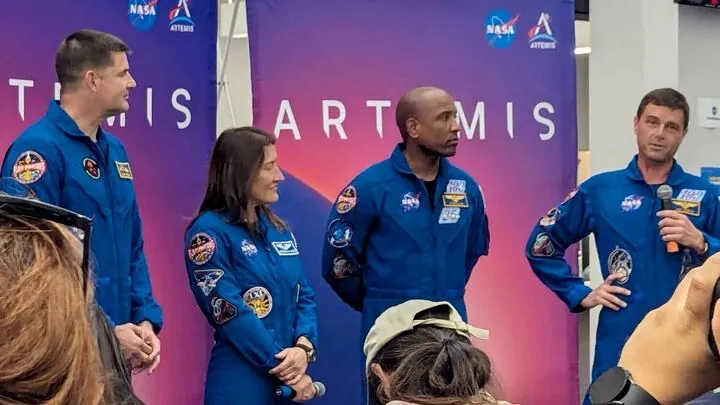

NASA's Artemis 2: Astronauts Become Living Science Experiments on Lunar Mission!
2025-09-17
Author: Nur
Groundbreaking Research in Space!
In an exciting twist for the upcoming Artemis 2 mission, NASA astronauts will not only explore the moon but also serve as vital subjects in groundbreaking health studies. Their crucial role will shed light on how sleep, stress, and radiation affect human health in the depths of space.
First Crewed Flight Test of Orion and SLS
Set to launch next year, Artemis 2 marks a pivotal moment in NASA's Artemis program, designed to establish a sustained human presence beyond Earth. This mission will feature the first crewed flight of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The selected four-person crew will push the spacecraft to its limits in the cislunar environment while conducting important scientific investigations.
In-Flight Data Collection: A Historical First!
Astronauts will transform into living biomedical experiments, enabling NASA to collect vital in-flight data about human resilience beyond low Earth orbit for the first time in over 50 years. These findings will significantly enhance our understanding of the biological impact of microgravity, building on decades of research from the International Space Station (ISS).
Comprehensive Health Monitoring
Leading up to the mission, astronauts will have their blood, urine, and saliva sampled, creating a rich dataset to monitor the effects of space travel on cardiovascular health, nutrition, immunity, and stress management across different mission stages.
The ARCHeR Project: Sleep and Stress Under Scrutiny!
The Artemis Research for Crew Health and Readiness (ARCHeR) project promises to reveal how an extended stay in the confined spaces of Orion impacts crew dynamics. Wearing wrist sensors, astronauts will track their movement and sleep patterns during the mission. Analyzing pre- and post-mission evaluations alongside in-flight data will provide crucial insights into the effects of deep space environments on alertness and teamwork.
Immune System Surveillance During Space Travel
Saliva samples collected throughout the mission will help researchers assess the astronauts' immune responses, especially to space radiation. Ingeniously, crew members will use specialized dab papers to store saliva samples, which will provide insights into dormant viruses potentially reactivated by the stress and microgravity conditions of space.
Innovative AVATAR Study: Miniature Organ Insights!
The mission will also involve "avatars"—miniature models of the astronauts' blood samples grown to mimic bone marrow on organ-on-a-chip devices. As these chips journey through the Van Allen belts, researchers aim to determine how bone marrow responds to the unique challenges of space radiation and microgravity, comparing results to existing data from the ISS.
Vigilant Radiation Monitoring!
Artemis 2 will employ a streamlined set of radiation sensors, with six active sensors inside Orion's cabin alongside personal dosimeters worn by the crew. These tools will monitor ongoing radiation levels and detect sudden surges during solar storms. In the event of dangerous readings, astronauts can quickly construct makeshift radiation shields using available materials onboard for added protection.
A New Frontier in Human Space Exploration!
With Artemis 2's innovative study of human health in space, NASA is not just paving the way for lunar exploration but is also unlocking the mysteries of human biology in extreme environments. This mission could redefine our understanding of long-duration space travel, making it wholly possible for humanity to venture further into the cosmos!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)