
Mysterious Sphere-Studded Rock Discovered by NASA's Perseverance Rover on Mars!
2025-03-26
Author: Wei Ling
Groundbreaking Discovery by NASA's Perseverance Rover
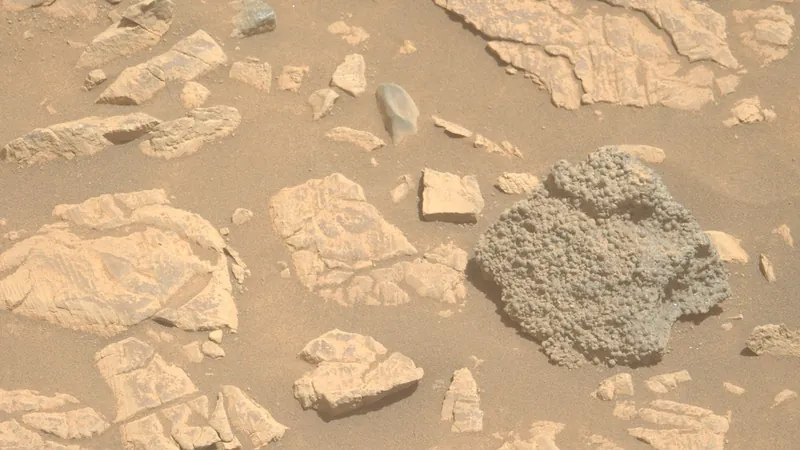
NASA's Perseverance rover has made yet another groundbreaking discovery on the surface of Mars, unveiling a fascinating rock formation that has left scientists scratching their heads. Dubbed "St. Pauls Bay," this peculiar rock features hundreds of dark gray spheres, each about the size of a millimeter, some adorned with tiny pinholes, giving it an otherworldly appearance.
Location and Significance of St. Pauls Bay Rock
This intriguing rock was found on March 11 along the rim of Jezero Crater, an ancient lakebed that has been the primary focus of the rover's explorations since 2021. The mission aims to uncover signs of past microbial life and understand the geological history of Mars. As these features are studied, scientists hope to gain crucial insights into how the region’s geology has evolved over billions of years.
Geological Context and Origin
In an official statement, the Perseverance team highlighted the significance of the St. Pauls Bay rock, emphasizing that understanding its geological context is fundamental to determining its origin and implications for the history of the Jezero Crater. Located on the slopes of the scientifically rich Witch Hazel Hill, which spans over 330 feet (101 meters) and acts as a layered record of Mars’ past, this rock might even have travelled from another location.
Comparisons with Previous Rover Discoveries
Interestingly, Perseverance is not the first rover to encounter such textured rocks. Previous missions, including those of the Opportunity and Curiosity rovers, have reported similar formations near their landing sites. These earlier observations led scientists to propose that these rocks may have formed through the interaction of groundwater moving through rock pores, a process which last year prompted Perseverance to identify popcorn-like formations potentially formed by ancient water flow.
Possible Formation Mechanisms
However, the journey to uncover the St. Pauls Bay rock’s origins is not cut and dry. It could also be the product of volcanic activity, resulting from rapid cooling of molten droplets, or even a consequence of meteorite impacts that vaporize surrounding rock, only for the vapor to condense and form new structures.
Commitment to Investigation
“Each formation mechanism presents its own unique implications for the evolution of these geological features," the mission team noted, emphasizing their commitment to thoroughly investigating this rock's history.
Future Explorations and Sample Collection
Currently, Perseverance is embarked on a bonus mission to delve deeper into the mysteries of Jezero Crater's rim, a region believed to have been shaped by Martian groundwater interactions, differing greatly from what has been explored on the crater's floor. The rover has begun collecting samples—some showing striking patterns reminiscent of leopard spots and poppy seeds—that may provide evidence of ancient microbial activity. These samples are carefully stowed in 30 cigar-sized tubes and await eventual retrieval by NASA's ambitious Mars Sample Return mission, which is expected to bring Martian samples back to Earth for detailed analysis.
Conclusion
Stay tuned as we continue to follow the incredible journey of Perseverance and its quest to unlock the secrets of the Red Planet! What revelations lie ahead? The adventure is just beginning!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)