Mysterious Icy Objects in the Milky Way Leave Astronomers Baffled!
2025-01-28
Author: Rajesh
Astronomers' Discovery in the Milky Way
A team of astronomers from the University of Tokyo and Niigata University has stumbled upon a baffling discovery—peculiar embedded icy objects located thousands of light years away from Earth. This trio, comprising Takashi Shimonishi, Itsuki Sakon, and Takashi Onaka, recently shared their groundbreaking findings on the arXiv preprint server, sparking intrigue within the scientific community.
Detection and Analysis
These peculiar objects were initially detected in 2021 from data collected by the AKARI space telescope between 2006 and 2011. However, the team faced a conundrum when these icy objects could not be accurately identified, compelling them to await additional observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) located in Chile. Unfortunately, the new data has only deepened the mystery surrounding their nature.
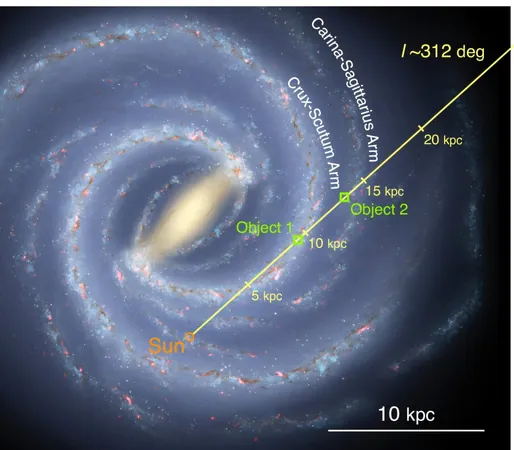
Characteristics of the Objects
The astronomers discovered that these two objects, while neighboring each other in the night sky, are actually separated by vast distances. Their analysis suggests these icy entities may be large ice balls, resting in the outer regions of the Milky Way. While they speculate that these could potentially be dense gas clouds or an undiscovered type of star, they dismiss the latter possibility due to their location far from typical star-forming regions in the galaxy.
Infrared Observations
Interestingly, infrared observations revealed that these entities have absorbed dust and ice—characteristics often found in young stellar objects or background stars obscured by thick gas clouds. Compounding the mystery, however, is the conflicting distance measurements: one object is recorded at 6,500 light years away by one telescope, while another source places it at an astonishing 30,000 light years from Earth. Despite these discrepancies, both sources consistently report the other object to be around 43,700 light years away.
Size and Composition
Moreover, both of these celestial enigmas appear to be nearly ten times the size of our solar system, a small scale considering they may be gas clouds. Preliminary data also indicate that the gas enveloping these objects is primarily composed of silicon dioxide, with traces of carbon dioxide—similar to the composition found in young stellar environments.
Future Investigations
As these researchers wrap up their analysis, they emphasize that existing data alone cannot conclusively identify either object, leaving the astronomical community in suspense. They are eagerly anticipating clearer insights when the James Webb Space Telescope is aimed at these mysterious icy bodies, hoping that it will unlock the secrets of their origins and provide answers to the questions they’ve raised.
Conclusion
Could these icy objects hold clues to the early formation of the Milky Way or provide insights into the elusive dark matter? Only time and advanced telescopes will tell! Stay tuned—this captivating saga is far from over!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)