Measles Outbreak Alert: Uncovering the Rise and New Variants in Lazio, Italy
2025-08-21
Author: Daniel
A Surge in Measles Cases Shakes Europe
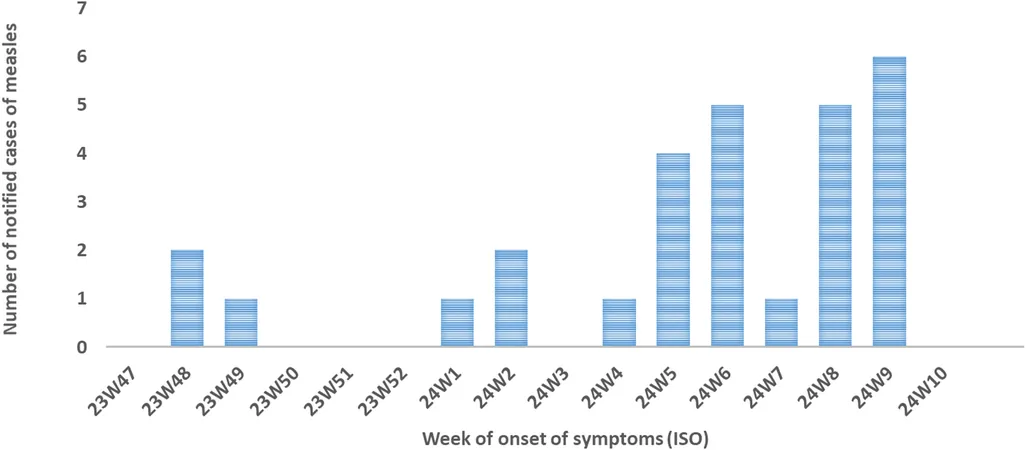
As the years 2023-2024 unfold, Europe is facing a troubling wave of measles cases, with outbreaks surging and new viral strains appearing that could undermine our diagnostic tests. In Lazio, Italy, a dedicated team of scientists set out to evaluate the alarming rise in measles cases between September 2023 and March 2024 using state-of-the-art molecular techniques.
Investigative Methodology
In this comprehensive study, researchers collected samples through routine measles surveillance, conducting tests for IgM, IgG, and utilizing Real-Time PCR for virus detection. The high-titer samples underwent whole-genome next-generation sequencing (WG-NGS) to provide insights into mutations and how they relate to phylogenetic relationships.
Encouraging Yet Concerning Findings
Out of 39 suspected measles cases, 28 were confirmed positive, with 82% classified as endemic cases. Despite a robust diagnostic approach, a worrying three-nucleotide mutation was detected in some strains, raising questions about the reliability of current testing methods. Fortunately, existing PCR tests still performed well against these mutated forms, detected accurately even at low concentrations.
Epidemiology Meets Genomics
The phylogenetic analysis revealed four distinct clusters, with a majority identifying sporadic cases tied to various outbreaks. Critically, this genomic approach allows for better tracing of transmission routes, crucial in a public health crisis. The researchers highlighted a significant finding: many cases were linked directly to unvaccinated individuals.
A Public Health Wake-Up Call
With vaccination rates plummeting, the risk of further outbreaks looms large. Countries across Europe, including Italy, are being urged to ramp up vaccination campaigns and strengthen their surveillance systems. The study emphasizes how genomic sequencing can play a pivotal role in informing effective health strategies.
The Bigger Picture: Vaccination Crisis Unveiled
Despite a safe and cost-effective vaccine available since 1963, measles continues to claim lives, particularly in unvaccinated populations. A startling statistic emerged: in 2024 alone, Europe reported over 125,000 cases—a staggering increase from the previous year, with many requiring hospitalization. The data calls for urgent action in reinforcing vaccination initiatives across all demographics.
Looking Ahead: The Path Forward
This research underlines the necessity of integrating molecular surveillance into public health response frameworks. By identifying transmission chains and outbreak clusters, authorities can implement more targeted intervention strategies to combat this persistent public health threat, ensuring a more vigilant and prepared response to future outbreaks of measles.
In Conclusion: Action is Vital
The rise in measles cases in Lazio is not just an isolated incident; it reflects a growing trend across Europe. With genomic surveillance proving its worth, public health officials must act swiftly to prevent measles from regaining a foothold. Strengthening immunization efforts and utilizing advanced sequencing techniques are crucial steps in the fight against this highly contagious virus.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)