
Mars' Atmosphere Loss Uncovered: Is Sputtering the Culprit?
2025-05-30
Author: Sarah
Mars: Once a Water World?
Did you know Mars was once a much livelier planet, teeming with liquid water and warmer climates? Far from the desolate landscape we see today, ancient Mars resembled Earth in its youth.
The Great Disappearance: Where Did the Atmosphere Go?
But what happened to Mars’ atmosphere? A groundbreaking mission by NASA has cracked the mystery wide open, revealing stunning insights into this cosmic puzzle.
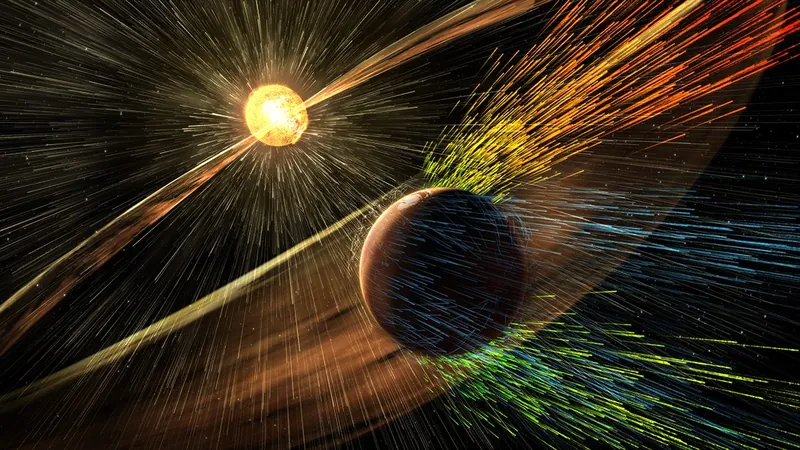
Unveiling the Process: 'Sputtering'
Enter 'sputtering' – a term that describes the atmospheric stripping process that scientists had theorized for years but never observed until now. Thanks to the MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere Volatile Evolution) mission, researchers can finally witness this phenomenon firsthand.
The Role of Solar Wind in Atmospheric Loss
Mars’ global magnetic field faded away early in its history, leaving it exposed to the relentless solar winds—streams of charged particles from the sun that can wreak havoc on a planet's atmosphere. As the winds blew, Mars lost the ability to hold its water. The longer it was battered by these solar forces, the more fragile its atmosphere became.
How Sputtering Works: A Dramatic Splash!
So, what is sputtering in layman’s terms? Imagine doing a cannonball into a pool, says Shannon Curry, principal investigator of MAVEN. The heavy ions crashing into the atmosphere create splashes of atoms and molecules, effectively vacuuming them into space.
Direct Evidence: A Game-Changer for Mars Research
Before MAVEN, scientists relied on indirect indicators like the unusual patterns of argon isotopes on Mars. Missing lighter isotopes raised many questions, and sputtering emerged as the prime suspect. Now, with MAVEN’s advanced tools, researchers created a 3D 'sputter map' of the Martian atmosphere. The findings showed bursts of argon precisely where solar particles impacted.
The Shocking Truth: Sputtering Happens Faster Than We Thought!
Even more astonishing, sputtering was found to be happening four times quicker than anticipated, and during solar storms, that rate accelerates even further.
Implications for Life on Mars
Understanding water's historical role on Mars is crucial for exploring the possibility of life beyond Earth. The revelations from the MAVEN mission underscore sputtering's significant impact on the Red Planet's climate evolution and its capacity to support life in the past.
A Major Breakthrough in Space Exploration
The findings from this pivotal research, published in Science Advances, not only illuminate how ancient Mars may have been a habitable world but also serve as a cautionary tale: atmospheres in space are delicate and vulnerable to the cosmos' harsh realities.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)