
Major Leap in Carbon Cycle Understanding: ESA's Biomass Mission Set for 2025 Launch!
2025-01-17
Author: Arjun
Introduction to the Biomass Mission
The European Space Agency (ESA) is gearing up for a groundbreaking initiative—the Biomass mission, slated to launch in 2025. This ambitious project aims to provide unparalleled insights into forest biomass, significantly advancing our understanding of the carbon cycle amidst growing environmental concerns.
Importance of Forests in the Carbon Cycle
Forests are vital carbon sinks, absorbing and storing substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2). However, ongoing issues such as deforestation and forest degradation are releasing this stored carbon back into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change. To combat this, it's crucial to accurately quantify global biomass to address these urgent issues.
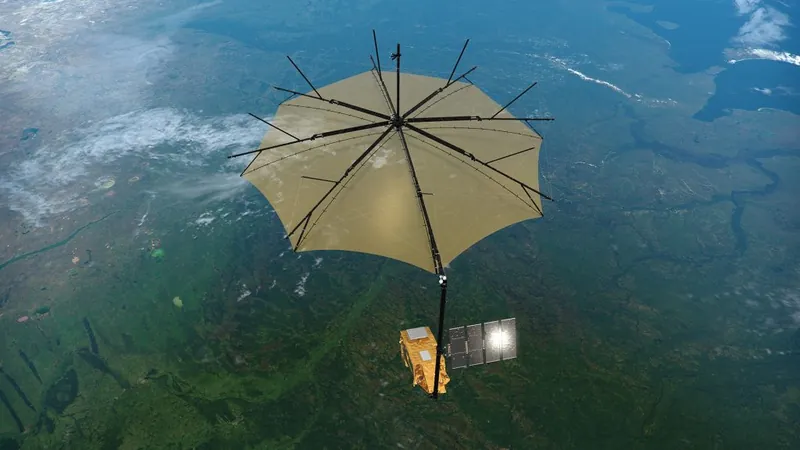
Innovative Technology: Satellite with SAR Instrument
The Biomass mission will pioneer a state-of-the-art satellite equipped with a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) instrument. This innovative technology is designed to measure forest height and above-ground biomass from space, even penetrating dense canopies and cloud cover—two major obstacles in forest research.
Collaborative Efforts in Satellite Construction
The satellite's construction involves the collaborative efforts of over 50 companies, spearheaded by Airbus UK. It's set to launch in April 2025 aboard the Vega-C rocket from Kourou, French Guiana, a significant boost to Europe’s space capabilities.
Insights from ESA's Project Manager
Speaking with Michael Fehringer, ESA's Biomass Project Manager, he emphasized the mission's role in clarifying uncertainties surrounding carbon storage in forests. While we have a grasp on fossil fuel consumption and resulting CO2 emissions, the fate of this carbon remains largely elusive. It could either linger in the atmosphere, be absorbed by oceans, or be taken up by plants, mostly in tropical forests. The mission seeks to identify how much carbon is sequestered in forests and how this changes over time—an essential element in climate modeling.
Measuring Carbon Through Biomass Density
One of the mission’s primary objectives involves estimating carbon through biomass density, converting wood mass into carbon equivalency. This will be tracked globally, with initial measurements capturing the state of Earth’s forests, followed by subsequent assessments to determine growth or loss of biomass.
The Journey to the Biomass Mission
The concept of the Biomass mission originated as early as 2005, navigating through competitive evaluations to secure its current status with a contract awarded to Airbus in 2016. Despite encountering technological hurdles, particularly with the development of the radar instrument, the team persevered. The COVID-19 pandemic further complicated progress, extending the timeline significantly; however, they are now back on track and prepared for the launch.
Commissioning Phase Post-Launch
Following the satellite’s deployment, a critical six-month commissioning phase will commence. This entails rigorous system checks and data acquisition to ensure the accuracy and functionality of the radar. This phase will also involve the calibration of instruments, cross-referencing with ground measurements collected by researchers on the field to validate the satellite’s findings.
Conclusion: A Pivotal Journey for Earth’s Climate
As the world watches closely, the Biomass mission is not just an endeavor into space but a vital step towards understanding the delicate balance of our carbon cycle. Will this mission unlock the secrets of our planet's forests? Stay tuned for updates as ESA embarks on this pivotal journey!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)