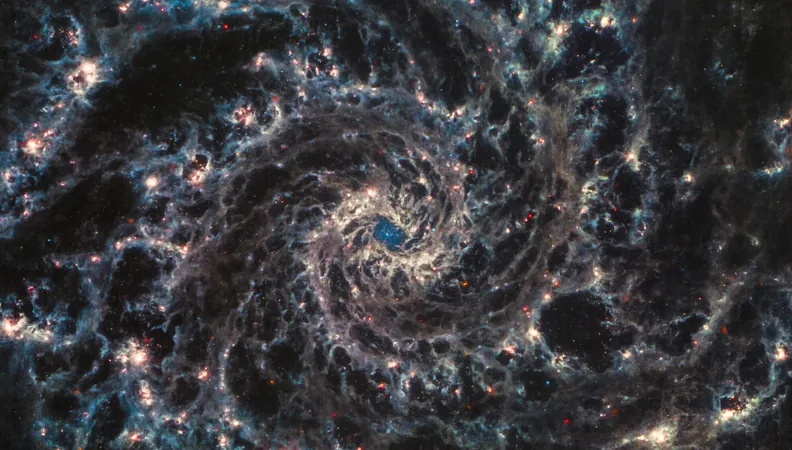

James Webb Telescope Confirms Revolutionary Galaxy Model: What This Means for Our Understanding of the Universe!
2024-11-02
Author: Wei Ling
Astronomers have an unparalleled advantage: the ability to look back in time. Given that starlight takes time to travel to Earth, we can study the cosmos’ history by capturing the light emitted by distant galaxies. This powerful capability is exemplified by instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which is transforming our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution. A recent groundbreaking study utilizing JWST has confirmed a longstanding model that has significant implications for astrophysics.
The Question of Chemical Enrichment
The focus of this study revolves around a crucial question: how do galaxies become chemically enriched? In the early universe, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, massive stars formed with no accompanying planets. After a brief but vigorous existence, these stars would die explosively, enriching their surroundings with heavier elements like carbon and oxygen, thereby facilitating the formation of more complex stars and planetary systems over generations.
Competing Theories of Enrichment
Historically, two competing theories have grappled for dominance in understanding this chemical enrichment. One theory emphasizes that the most massive stars are the key players. Their dramatic supernova explosions eject their enriched outer shells into the cosmos, mixing with interstellar material and allowing new stars to form. On the other hand, a rival theory put forth around two decades ago posits that smaller, sun-like stars are the real heroes of chemical enrichment.
Unlike their massive cousins, sun-like stars do not meet their end in powerful explosions. Instead, they evolve into red giants, undergoing a transformation that involves the fusion of helium in their cores. Known as asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars, these bodies may contribute less material to space individually, but because they are far more numerous, some scientists argue that they may collectively have a greater impact on cosmic chemistry.
Challenges in Disentangling the Models
Disentangling these models has posed a challenge to astronomers. Supernovae are easy to detect, even at vast distances of billions of light years, but AGB stars are much harder to observe. This is where the JWST has made a monumental breakthrough, allowing scientists to test the AGB theory rigorously.
Revolutionary Findings with JWST
Using the JWST, researchers analyzed the spectra of three young galaxies. The telescope’s NIRSpec camera captures high-resolution infrared spectra, enabling scientists not only to detect specific elements but also to assess their relative abundances. The findings were remarkable: there was a pronounced presence of carbon and oxygen, characteristic of AGB remnants, alongside rarer elements such as vanadium and zirconium. These observations point strongly towards the involvement of a special category of AGB stars known as thermally pulsing AGBs, or TP-AGBs.
TP-AGBs undergo a unique pulsing phase in their late evolutionary stages. The cycle involves alternating phases of expansion and contraction within the star, significantly enhancing its ability to eject enriched material into space. This new study strongly suggests that these stars play a pivotal role in enriching galaxies, potentially validating the AGB model that has been under discussion for the last 20 years.
Implications for Our Understanding of the Universe
What does this confirmation mean for our understanding of the universe? It indicates that the process of chemical enrichment is more nuanced and complex than previously thought. By appreciating the contribution of AGB stars, we can gain deeper insights into the life cycles of galaxies and the chemical evolution of the cosmos.
As the JWST continues to unravel the mysteries of the universe, we are reminded that there is still so much to discover. Each observation not only challenges our previous assumptions but also opens new avenues of inquiry into the nature of the galaxy. Stay tuned, as the cosmos has more secrets waiting to be uncovered!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)