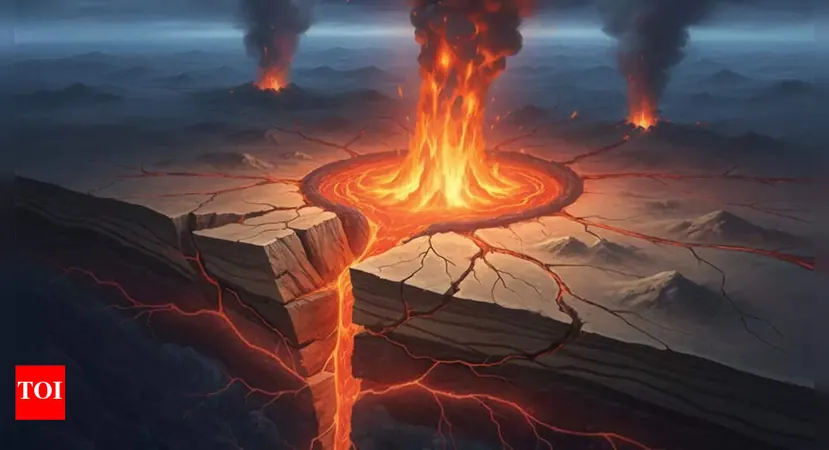

Is Africa on the Brink of Splitting Apart? Discover the Shocking Geological Heartbeat Beneath!
2025-09-11
Author: Ming
A Groundbreaking Discovery in Eastern Africa
In a stunning revelation, scientists have unearthed a remarkable geological phenomenon deep beneath eastern Africa, known as a "geological heartbeat." This incredible process is driven by rhythmic pulses of molten rock surging from the Earth’s mantle, significantly weakening the crust and paving the way for earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Over the course of millions of years, this dynamic activity could lead to a dramatic split of the African continent, ultimately giving rise to a new ocean basin.
The Afar Triple Junction: Where Earth's Forces Collide
At the heart of this geological spectacle lies the Afar Depression in Ethiopia, a unique region where three major tectonic rifts intersect: the Red Sea Rift, the Gulf of Aden Rift, and the Main Ethiopian Rift. This volatile area, termed a "triple junction," is notorious for its frequent seismic tremors and volcanic eruptions, and researchers have now uncovered the vital role of a rising mantle plume that pulses rather than flows continuously.
Unmasking the Heartbeat of the Earth
By studying lava samples from over 130 recent volcanoes, scientists have identified chemical signatures that indicate this mantle does not move in uniform currents. Instead, it rhythmically pulses, akin to a heartbeat, and these surges accelerate the rifting process, setting the stage for what may become one of the most significant geological transformations in human history.
The Future of Africa: A Land Transformed
As these geological forces slowly but surely pull the Somali Plate away from the larger Nubian Plate, deep rift valleys are expected to emerge over several million years. Eventually, seawater from the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden will flood into these depressions, creating a massive new ocean. This unprecedented change could turn landlocked nations like Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo into vital coastal territories.
The Broader Implications of This Discovery
This groundbreaking study reshapes our understanding of the intricate relationship between deep mantle activities and tectonic plate interactions. Similar geological processes in history contributed to the formation of the Atlantic Ocean when South America separated from Africa. Moreover, active mantle upwellings, such as those in Afar, can release significant quantities of gases that may influence global climates and even instigate mass extinctions. Researchers stress that while Africa's division will unfold over millions of years, it serves as a poignant reminder of the Earth's slow yet transformative power.
Future research aims to further dissect the mantle flow beneath the thin tectonic plates, enhancing predictions for volcanic activity and seismic events. For now, scientists remain in awe of the Earth's hidden rhythms—a geological heartbeat potent enough to reshape a continent and herald the birth of a new ocean.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)