Incredible Discoveries on the Ultra-Hot Neptune LTT 9779b: Clouds and Heat Patterns Revealed!
2025-01-28
Author: Sarah
Recent Discoveries
Recent research has unveiled astonishing details about the ultra-hot Neptune LTT 9779b, revealing a complex atmospheric dynamic characterized by unique circulation patterns and intriguing cloud formations. Scientists have long theorized that gas giant exoplanets, especially those exposed to intense irradiation, exhibit circulation dominated by day-to-night heat transport. However, the specific behaviors of these planets, particularly ultra-hot varieties like LTT 9779b, have remained largely uncharted—until now.
Methodology and Observations
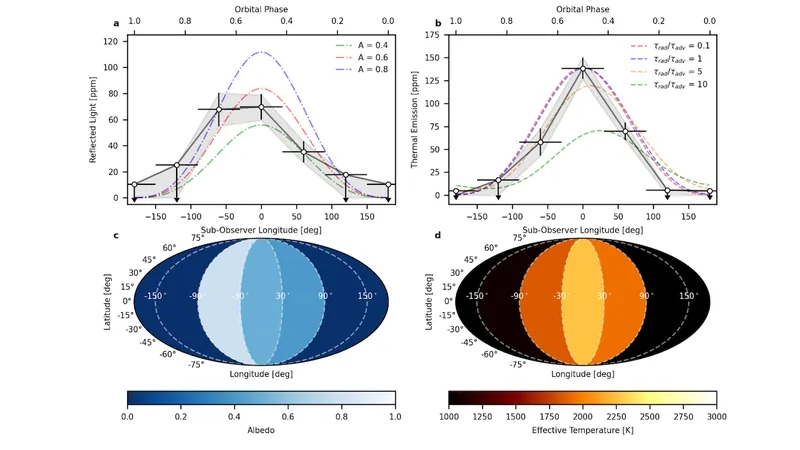
Using the James Webb Space Telescope's Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (NIRISS/SOSS), a team of astronomers conducted phase-resolved reflected light and thermal-emission spectroscopy. They monitored LTT 9779b's entire phase curve from 0.6 to 2.8 µm. The results were nothing short of spectacular, revealing an asymmetric dayside in reflected light, indicative of high reflectivity with striking white clouds on the western side. In contrast, the eastern dayside displayed a significantly lower albedo, leading to an overall average dayside albedo of 0.50.
Temperature Variations
One of the most fascinating findings pertains to the temperature variations across the planet. The thermal phase curve indicates a marked temperature difference, with the effective temperature on the dayside reaching a sweltering 2,260 K, while the cold nightside temp drops below 1,330 K, showcasing rapid radiative timescales—factors critical to understanding the planet's atmosphere.
Atmospheric Circulation and Cloud Formation
The team proposed a distinctive model of atmospheric circulation: heat from the intensely lit dayside is transported eastward to the cooler nightside by a powerful equatorial jet. This process not only redistributes heat but also results in a cooler western dayside, creating ideal conditions for the condensation of silicate clouds, a phenomenon that could reveal the presence of exotic minerals in the atmospheres of these distant worlds.
Cloud Dynamics
The transitions between cloudy and cloud-free regions further illustrate the complexities of LTT 9779b's atmosphere. The researchers created a detailed schematic displaying temperature and cloud coverage, aligned with their observations of the planet's six orbital phases. This information is crucial not just for LTT 9779b but opens doors for understanding the atmospheres of similarly situated exoplanets.
Significance and Future Exploration
The implications of this research extend beyond mere curiosity, as it enhances our understanding of planetary atmospheres and the potential for cloud formation in extreme environments. There's still a world of exploration to be done in the realm of gas giants, especially among those with unique heat profiles—stay tuned as astronomers continue to probe the mysteries of our galaxy's most extreme planets!
Conclusion
This groundbreaking study represents a significant milestone in exoplanetary science, shining a light on the intricate relationship between temperature gradients and cloud formation. As we look ahead, the research into LTT 9779b may very well pave the way for future discoveries about the vast and varied atmospheres in our universe!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)