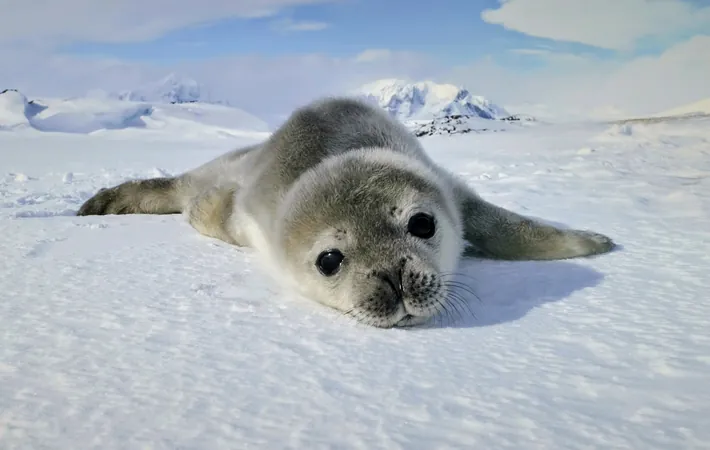

How Seal Pregnancies Could Revolutionize Human Birth Treatments
2025-04-16
Author: Jia
Nature's Survivors: Clues from the Ocean
Wild animals have evolved incredible adaptations to thrive in harsh environments. These adaptations might just hold the key to solving some pressing human reproductive health issues. Dr. Michelle Shero, an assistant scientist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, is at the forefront of this fascinating research, focusing particularly on the reproductive habits of seals.
The Surprising Link: Seals and Gestational Diabetes
Pregnancy for humans is laden with metabolic challenges, with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) affecting as many as 25% of pregnancies. While GDM typically resolves post-birth, it can leave lasting effects on both mother and child. Conventional treatments aim to manage glucose levels through diet, exercise, or medication. However, seals take a completely different approach.
Fasting for the Future: Seal's Unique Strategy
During reproduction, phocid seals, like Weddell and hooded seals, enter a state of fasting. They stop eating and can lose up to 40% of their body weight while nursing. Remarkably, both mothers and pups not only survive but thrive. This astonishing adaptation centers on a reversible form of insulin resistance that mimics GDM but is non-harmful.
Mastering Metabolism: Seal Survival Tactics
Unlike humans, seals maintain elevated blood sugar levels without developing harmful ketones or tissue damage. Their ability to balance low insulin levels while sustaining necessary glucose circulation is a masterpiece of hormonal regulation. This delicate equilibrium may offer insights to improve human treatments for gestational diabetes.
Harnessing Nutrients: How Seals Manage Glucose
In a fascinating twist, fetal glucose levels in Weddell seals surpass maternal levels, suggesting a controlled nutrient transfer that promotes fetal growth without overgrowth. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to groundbreaking advancements in managing human gestational diabetes.
Diving Deep: Seals and Hypoxia
Seals dive to extraordinary depths, holding their breath for hours while their bodies cleverly regulate oxygen supply. By prioritizing blood flow to essential organs like the brain and heart, they withstand oxygen deprivation that would incapacitate humans. Remarkably, their fetuses experience the same adaptations.
Revolutionizing Neonatal Care: Learning from Seals
Many infants face oxygen deprivation during birth, a condition that can result in lifelong harm. While methods like cesarean sections help mitigate this risk, seals demonstrate that repeated hypoxic conditions during pregnancy can be survived. Their unique adaptations could dramatically improve neonatal care and outcomes.
Pause, Don't Freeze: The Mystery of Embryonic Diapause
Seals also exhibit embryonic diapause, delaying embryo implantation until optimal conditions arise. This natural strategy could transform how we approach fertility and pregnancy in other mammals, including humans. Imagine being able to pause an embryo's development until the timing is just right!
The Future of IVF: Embracing Natural Mechanisms
Current in vitro fertilization methods rely on freezing embryos, often leading to DNA damage and reduced success rates. If scientists could harness the ability to induce a diapause-like state, it could revolutionize embryo implantation techniques, ensuring better outcomes.
The Takeaway: Embracing Nature's Solutions
Seals embody resilience and adaptability in the face of extreme conditions. Their biological secrets could reshape our understanding of health and pregnancy, challenging the notion of what 'normal' should be. Dr. Shero emphasizes the importance of learning from the extraordinary capabilities of wildlife to inspire innovative solutions for human health. As we delve deeper into these marine mysteries, the potential to revolutionize reproductive medicine may be on the horizon.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)