How COVID-19 Disrupted Colorectal Cancer Screening: Key Insights from Recent Studies
2025-03-26
Author: Wei Ling
The Importance of Colorectal Cancer Screening
Colorectal cancer, which originates in the colon or rectum, is a leading health crisis—often ranking as the second most common cancer in the United States and the second primary cause of cancer-related fatalities. According to the American Cancer Society, approximately 52,900 deaths are projected from colorectal cancer in 2025. Regular screening is crucial for early detection, which can drastically improve treatment outcomes and survival rates.
A Closer Look at Screening Trends During the Pandemic
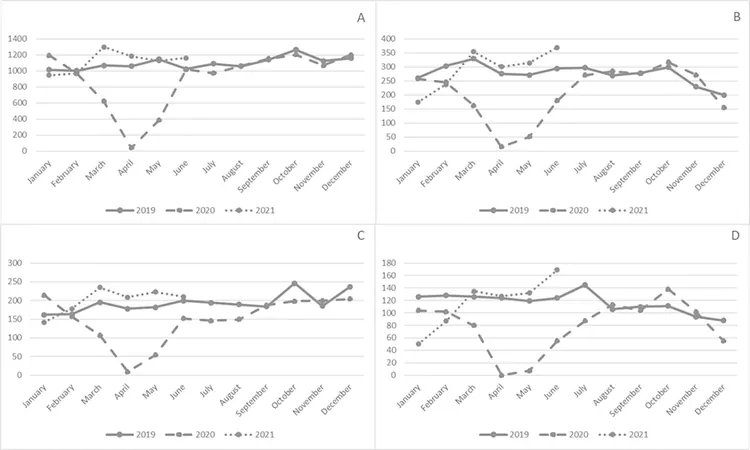
Analysis over a 30-month period surrounding the first 18 months of the COVID-19 pandemic revealed a troubling trend for colorectal cancer screening, notably colonoscopies. Research indicates that there was a sharp decline in screening procedures during April 2020, when many facilities ceased operations due to COVID-19 restrictions. Senior researcher Dr. Thomas F. Imperiale noted that there were literally no screening colonoscopies performed during April of 2020, highlighting the critical challenges faced by healthcare providers during the pandemic.
However, the resilience of the healthcare system became evident as screening volumes rebounded swiftly within months. Non-invasive tests, such as FIT (Fecal Immunochemical Tests) and FIT/DNA tests, also experienced declines but showed faster recovery rates. Notably, the overall colonoscopy volume decreased by about 19% in 2020 compared to 2019, but returned to baseline levels in 2021 without significant differences in the detection rates of early versus late-stage cancers.
The Role of Telehealth in Colorectal Screening
Dr. Imperiale stressed the potential for telehealth and remote monitoring technologies to bridge gaps in cancer screening and diagnosis moving forward. As healthcare systems navigate future disruptions—be they pandemics, natural disasters, or other emergencies—the flexibility and accessibility of telehealth services will become increasingly invaluable. We need to develop or maintain these technologies to ensure that preventive services remain available for those who cannot or do not wish to meet in-person with healthcare professionals, he emphasized.
Ensuring Follow-Up Care for Patients
Interestingly, while there was a mild delay in follow-up diagnostic colonoscopies after positive non-invasive screenings in 2020 compared to earlier years, the proportion of patients completing these procedures remained robust, above 70%. This statistic highlights the prioritization of diagnostic colonoscopies among healthcare providers during the pandemic, as evidenced by similar trends observed nationwide.
The research outlined not only underscores the impact of COVID-19 on colorectal cancer screenings but also indicates a critical need to enhance public health campaigns aimed at promoting non-invasive testing options and ensuring adequate access for those who require further diagnostic colonoscopies after initial screenings.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned for Future Pandemics
The findings from these studies call for an urgent conversation about how healthcare systems can adapt and improve cancer screening processes in the face of future health crises. With effective strategies to mitigate disruptions and maintain the momentum of preventive care, the ongoing battle against colorectal cancer can be significantly strengthened. Continuous evaluation and adaptation are essential to ensure that patients receive timely care, especially during challenging times.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)