Groundbreaking Study Uncovers How Tidal Forces Influence Earthquake Fault Zones!
2025-05-30
Author: Mei
Unlocking the Secrets of Earthquakes
Seismology is at the forefront of understanding earthquakes, the natural disasters that shape our planet. Researchers aim to identify precursors to these catastrophic events by closely monitoring the stress within fault zones, thus paving the way for effective earthquake prevention strategies.
The Challenge of Measuring Stress
Directly measuring stress in fault zones is notoriously challenging. However, scientists have found a promising alternative: observing changes in seismic wave speeds. By monitoring these variations over time, they can glean critical insights into the underlying geological conditions.
A Revelatory Study from China
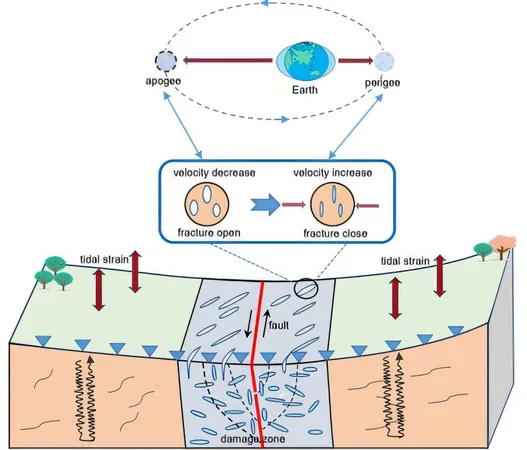
In a groundbreaking study published in the prestigious National Science Review, Professor Yao Huajian and his team from the University of Science and Technology of China revealed astonishing findings about the impact of tidal forces on seismic wave speeds in the Anninghe fault zone, located in the rugged Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
Cutting-Edge Technology in Action
Utilizing a dense seismic array and advanced seismic interferometry techniques, the research team meticulously analyzed continuous noise data to calculate how seismic wave velocities fluctuate in this crucial fault zone. Their findings showed that these velocities exhibit remarkable diurnal and semi-diurnal patterns, particularly pronounced within the fault's fracture zone.
Tidal Forces: The Hidden Variables
After isolating environmental factors, the team identified significant monthly cycles of wave speed changes. When comparing their data with theoretical tidal strain, they found a strong correlation, highlighting how tidal forces are key players in this seismic dance.
Amplification Effects Unveiled
Employing the standard spectral ratio method, researchers assessed the east-west movements caused by local and distant earthquakes. They discovered that the fault fracture zone exhibited a strikingly higher amplitude spectrum ratio, indicating a greater degree of medium fragmentation than in surrounding areas.
Micro-Cracks in Action
The tidal forces influence seismic wave velocities by periodically opening and closing micro-cracks within the underground medium. As these cracks open, wave speeds decrease; conversely, they increase when the cracks close. This sensitivity to tidal forces results in more significant changes in the fault fracture zone.
A New Frontier in Earthquake Research
This innovative study not only sheds light on how tidal forces disrupt the internal stress fields of fault zones but also offers invaluable insights for developing dynamic geophysical observation systems in active fault regions. Such advancements could be pivotal in enhancing earthquake prediction and preparedness.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)