Groundbreaking Study Reveals Secret Mechanisms of Catechin Production in Tea Plants!
2024-09-23
Groundbreaking Study Reveals Secret Mechanisms of Catechin Production in Tea Plants!
New research has unveiled critical insights into catechin biosynthesis, a key process in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis), which is celebrated globally for its ability to produce tea rich in bioactive compounds. Catechins, the primary active compounds found in tea, are linked to numerous health benefits, including protective effects against serious conditions such as diabetes, cancer, and heart diseases.
Yet, these beneficial compounds are notoriously sensitive to environmental factors, particularly the availability of phosphate, which is often limited in the soils where tea is cultivated. This scarcity poses a significant threat to tea quality by disrupting essential metabolic pathways responsible for catechin accumulation.
Recognizing the pressing need to decipher the molecular dynamics of catechin production amidst nutrient fluctuations, Dr. Gaojie Hong and his team from the Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences took on this challenge. Their comprehensive study explored the intricate relationship between phosphate signaling and jasmonate pathways, key regulatory mechanisms in tea plants.
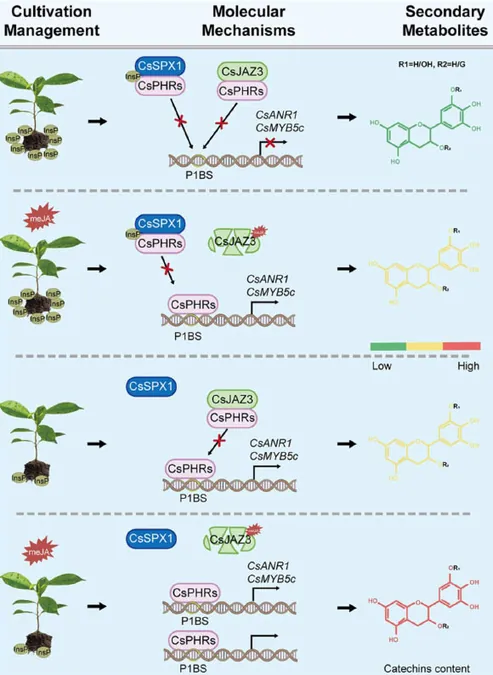
Remarkably, the researchers identified two transcription factors—CsPHR1 and CsPHR2—that play pivotal roles in phosphate signaling. These factors, alongside CsJAZ3, a crucial repressor in the jasmonate pathway, interact to regulate catechin biosynthesis as influenced by nutrient levels and hormonal cues.
The findings demonstrated that when phosphate levels are low, CsPHR1 and CsPHR2 activate essential genes such as CsANR1 and CsMYB5c, both integral to catechin production. Additionally, the study revealed that CsSPX1, a phosphate pathway repressor, modulates the effects of CsPHR1 and CsPHR2, thus finely tuning the plant's response to phosphate scarcity.
A fascinating interaction was uncovered between CsJAZ3 and the phosphate signaling factors, indicating a significant link between jasmonate signaling and phosphate regulation. This interplay is crucial for the plant's adaptive response to nutrient stress and hormonal variability, ultimately impacting catechin levels and tea quality.
"Our study unveils a complex regulatory network where phosphate and jasmonate pathways intersect to control catechin biosynthesis in tea plants," explained Dr. Hong. This groundbreaking understanding opens up exciting avenues for enhancing tea quality through targeted genetic modifications and refined environmental management practices.
As tea lovers around the world savor their brews, this research not only enriches our comprehension of tea metabolism but also lays the foundation for future innovations in the agricultural sector, with the potential to elevate the quality of one of the globe's most cherished beverages.
The findings of this compelling study were published in the esteemed journal Horticulture Research, making waves in the scientific community as it holds promise for improving tea quality and sustainability in agricultural practices worldwide.
Stay tuned for more news on how science is revolutionizing our favorite drinks!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)