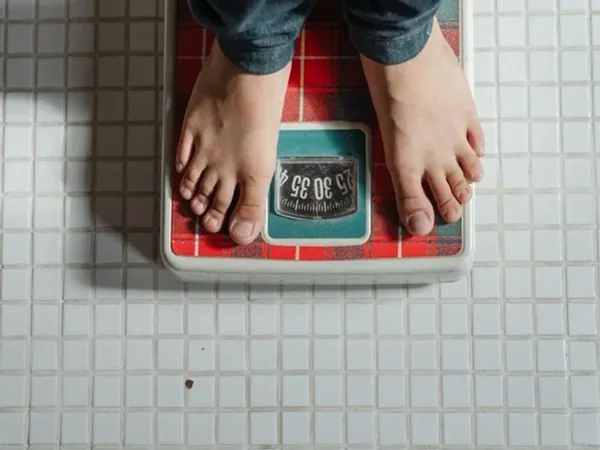

Groundbreaking Study Reveals Protein That May Preserve Muscle Mass During Weight Loss!
2025-01-26
Author: Arjun
Groundbreaking Discovery at Salk Institute
In a groundbreaking exploration published on January 22, 2025, scientists at the prestigious Salk Institute have unveiled a crucial protein named BCL6 that plays a pivotal role in maintaining muscle mass. This discovery comes at a time when many individuals are turning to weight loss medications like Ozempic, which belong to a class of drugs known as GLP-1s. As these medications have gained traction, there is an urgent need to understand how they affect muscle retention during fat loss.
Implications for Weight Loss Medications
The research indicates that individuals, especially those utilizing GLP-1 drugs, could potentially benefit from therapies designed to boost BCL6 levels. The study found that mice with reduced BCL6 exhibited a marked decrease in both muscle mass and strength. However, when BCL6 levels were restored, the mice successfully reclaimed their lost muscle. This raises exciting prospects for combining GLP-1 treatments with BCL6-enhancing medications, paving the way for a dual approach in combating muscle loss associated with weight management.
Broader Impacts on Muscle Health
Furthermore, the implications of this research extend beyond just those using weight loss drugs. The BCL6-boosting therapy could be transformative for older adults, who naturally experience muscle loss with age, and patients suffering from systemic diseases such as sepsis or cancer, where muscle wasting is common.
Expert Insights from Ronald Evans
Ronald Evans, a prominent professor and the director of the Gene Expression Laboratory at Salk, emphasizes the importance of muscle upkeep. "Muscle is the most abundant tissue in the human body, so its maintenance is critical to our health and quality of life," he states. His team's work sheds light on how muscle maintenance is intricately linked to nutrition and energy levels, giving scientists vital insights needed to create therapies for those grappling with muscle loss caused by various factors—be it weight reduction, aging, or illness.
Biochemical Pathways Explored
Interestingly, the research also delves into the biochemical pathways involved. Through a series of experiments, the team discovered that fasting stimulates the secretion of growth hormone, which subsequently reduces BCL6 levels in muscle cells. BCL6 is known to regulate SOCS2, and decreased levels of BCL6 result in lower SOCS2 expression. Without sufficient BCL6 to modulate SOCS2, the production of IGF1—a key growth factor—diminishes, ultimately leading to weaker and smaller muscles.
Significance of Muscle Mass Preservation
As muscle mass is vital not only for physical strength but also for overall metabolic health, these findings mark a significant step forward in the realm of muscle preservation. The possibility of enhancing muscle retention in various at-risk populations could revolutionize the approach to weight management, aging, and disease recovery.
Future Research Directions
Stay tuned for more updates as researchers continue to explore this fascinating link between BCL6, muscle mass, and effective therapeutic interventions!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)