Groundbreaking Study Reveals Hippocampus' Role in Mastering Complex Motor Skills!
2024-09-26
Introduction
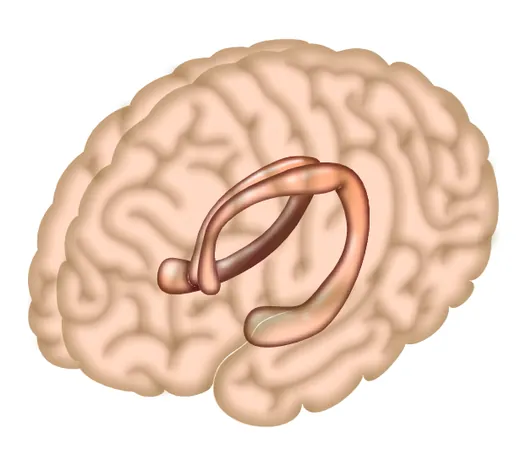
In a stunning revelation, researchers at the University of Birmingham have unearthed a previously unrecognized function of the hippocampus, linking it to the control of complex movements like handwriting, typing, and playing musical instruments. While the hippocampus has long been associated primarily with memory formation and spatial navigation, this groundbreaking study poses a significant challenge to that understanding and hints at transformative possibilities for rehabilitating individuals affected by neurological and neurodegenerative disorders.
Study Overview
Published in The Journal of Neuroscience, the study meticulously reanalyzed functional MRI (fMRI) data, directing their focus on critical subcortical brain regions as participants executed practiced finger movements on a force-sensitive keyboard in a manner akin to piano playing. The results were astonishing: while brain regions typically recognized for “muscle memory,” such as the basal ganglia and cerebellum, were active during these tasks, it was actually the hippocampus that contained vital information about the sequence of finger movements being performed.
Significance of the Discovery
This discovery enables predictions about upcoming actions based solely on activity in the hippocampus. For instance, researchers could differentiate whether a person intended to type 'fears' or 'fares' simply by analyzing hippocampal function. Such insight underscores a fascinating intersection between episodic memory—the ability to recall past experiences—and procedural memory, which governs learned skills.
Expert Insights
Dr. Katja Kornysheva, an associate professor and the study's senior author, emphasized the significance of this finding: “This result is interesting because it shows that the brain systems for episodic and procedural memory work together more than we thought. This is especially true when we need to remain flexible and switch between learned sequences, such as typing on a computer or collaborating in music.”
Future Implications
Moreover, former doctoral student Dr. Rhys Yewbrey, who led the research, added, “Our findings indicate that the hippocampus may be crucial for skilled and adaptable motor control, helping to outline a strategy for action. This newfound understanding could pave the way for the development of more effective training programs for neurological rehabilitation and could expedite the learning process for acquiring new skills.”
Conclusion
As the implications of this research unfold, it raises tantalizing questions about the scope of brain functionality and how we might harness these insights for therapeutic purposes. What does this mean for the future of skill acquisition and rehabilitation? One thing is certain: the hippocampus is more than just a memory center; it’s a pivotal player in mastering the art of movement! Stay tuned for more updates on this exciting area of research!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)