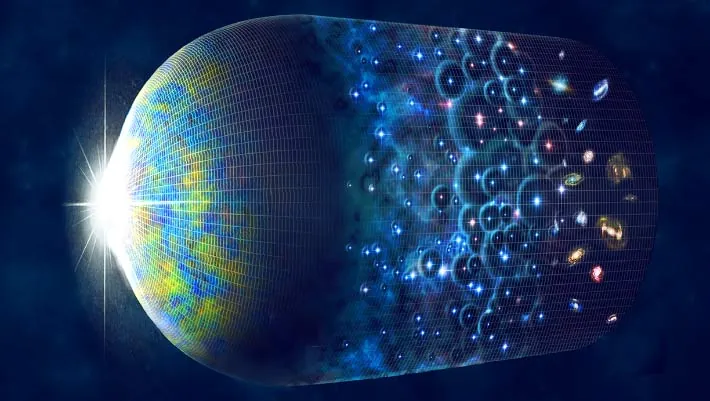
Groundbreaking New Findings Challenge Established Theory on Galaxy Formation!
2024-11-12
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
In a stunning revelation, recent research challenges the long-held beliefs about how galaxies formed in the early universe. According to data collected by the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, the expectations surrounding the role of dark matter in galaxy formation have been upended.
New Discoveries
Instead of dim signals from small, primitive galaxies, astronomers are encountering surprisingly large and bright galaxies that align with an alternative gravitational theory. Professor Stacy McGaugh from Case Western Reserve University, who led the research, stated, “What the theory of dark matter predicted is not what we see.”
Challenging Conventional Models
The prevailing lambda-CDM model, which relies heavily on dark matter to explain the gradual formation of galaxies from smaller structures, has encountered a reality check. Rather than the small, faint precursors expected, the Webb Telescope has revealed an early universe filled with substantial galaxies appearing much quicker than dark matter theories anticipated.
A New Perspective: MOND
This unexpected data suggests that a theory known as MOdified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND), posited more than twenty-five years ago, might provide a better explanation for the rapid formation of these massive galaxies. According to MOND, galaxies assembled much more rapidly and expanded outward with the universe, in stark contrast to the gradual buildup predicted by cold dark matter models.
Scientific Method in Action
McGaugh emphasized that the early universe's brightness and size reflect MOND’s predictions, saying, "The large and bright structures seen by Webb very early in the Universe were predicted by MOND over a quarter century ago.” He added, "I was raised to think that saying 'I told you so' was rude, but that’s the essence of the scientific method: make predictions and verify which come true."
Implications for Cosmology
What does this mean for our understanding of the cosmos? For years, astronomers leaned heavily on dark matter as the missing piece to explain how galaxies could form from an initially smooth universe. Yet, despite the comprehensive models, the evidence observed by Webb has compelled scientists to rethink.
The Role of the Webb Telescope
The Webb Telescope, which launched in 2021, was specifically designed to probe these fundamental questions: how and when did stars and galaxies emerge? As it continues to deliver unprecedented insights, astronomers are left with some critical challenges, particularly in finding a theory that reconciles both MOND with general relativity.
Conclusion
With this publication in the Astrophysical Journal, scientists are prompted to reevaluate existing hypotheses about the dawn of galaxies and potentially prepare for a paradigm shift in cosmology. As researchers delve deeper into this captivating cosmic mystery, the implications of such findings could significantly alter our understanding of the universe's formation and evolution.
Stay Tuned
Stay tuned for more updates on how these changes could unravel the secrets of our universe!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)