Groundbreaking Discovery: Scientists Unveil New Method to Induce Self-Destruction in Cancer Cells!
2024-11-03
Author: Daniel
Groundbreaking Discovery: Scientists Unveil New Method to Induce Self-Destruction in Cancer Cells!
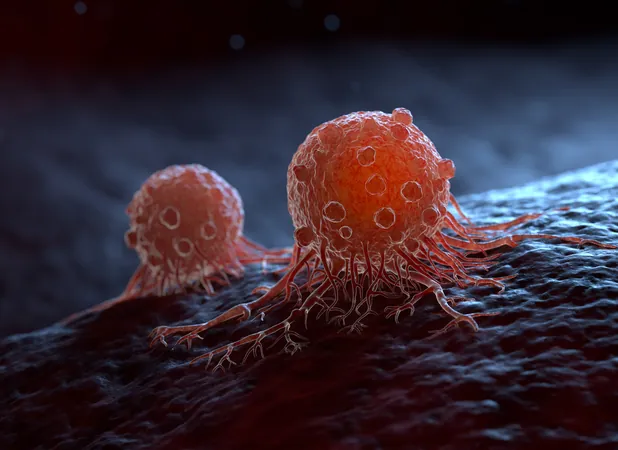
Scientists have achieved a remarkable breakthrough by developing a new compound that triggers cancer cells to self-destruct. This innovative solution, which consists of two interconnected proteins, was detailed in a recent paper published in the prestigious journal Science.
The inception of this compound stemmed from the insights of Gerald Crabtree, MD, a professor renowned for his work in developmental biology. He reflected upon the well-established concept known as apoptosis – a natural process where cells can initiate their own demise when deemed beneficial for the organism. This fascinating cellular mechanism plays a vital role in many biological processes, from embryonic development to the elimination of dysfunctional cells.
Current cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation tend to affect not only cancerous cells but also healthy ones, leading to severe side effects. This has prompted researchers to search for targeted therapies that can specifically eliminate malignant cells. The introduction of a method that allows cancer cells to trigger their own destruction is poised to revolutionize cancer treatment.
At the heart of this new approach is a protein called BCL6, which is notorious for its role in blood cancers like lymphoma. When mutated, BCL6 operates as an oncogene, meaning it promotes cancer progression by suppressing apoptosis-related genes—essentially granting cancer cells a form of immortality. However, in a groundbreaking twist, researchers discovered that when BCL6 is linked with another protein known as CDK9, it acts as a catalyst for gene activation. This unique combination effectively reactivates the apoptosis genes that BCL6 typically silences, initiating the self-destruction process in cancer cells.
In essence, the scientists turned a survival mechanism of cancer into a potent weapon against it. The research team is now conducting tests with this novel compound on mice diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Initial results are expected soon, and the scientific community eagerly anticipates breakthroughs that could pave the way for the next generation of cancer treatments.
Stay tuned for updates, as these findings may not only offer hope to countless patients but could also reshape the future of oncology!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)