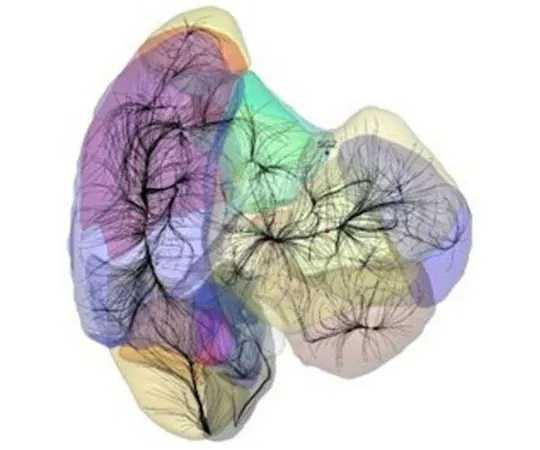
Groundbreaking Discovery Reveals Key Gravitational Structures in the Universe
2024-09-29
In a remarkable breakthrough, an international team of scientists has unveiled significant insights into the large-scale structure of the Universe by identifying essential gravitational regions known as "basins of attraction." This pivotal research was led by Dr. Valade in collaboration with esteemed mentors, including Prof. Yehuda Hoffman from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and Prof. Noam Libeskind from the AIP Potsdam. The efforts received substantial contributions from other notable researchers, such as Dr. Pomarede from the University of Paris-Saclay and Dr. Pfeifer from AIP Potsdam, alongside experts Prof. Tully and Dr. Kourkchi from the University of Hawaii.
Unraveling the Mysteries of Cosmic Structure
Rooted in the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (LCDM) cosmological model, this groundbreaking study suggests that the Universe's large-scale architecture evolved from quantum fluctuations that occurred during the tumultuous early stages of cosmic inflation. These minute density variations became the seeds for galaxies and galaxy clusters, eventually leading to the formation of gravitationally dominated regions termed "basins of attraction."
Harnessing Innovative Techniques with Cosmicflows-4 Data
Utilizing cutting-edge Cosmicflows-4 (CF4) data, the research team employed a Hamiltonian Monte Carlo algorithm to meticulously map the Universe's intricate structure, extending to nearly a billion light-years. This advanced method allowed researchers to demarcate gravitational domains more effectively, presenting a probabilistic model that outlines the major basins of attraction which govern the movements of galaxies.
Revised Perspectives on the Laniakea and Shapley Basins
Previously, the Milky Way was classified as part of the Laniakea Supercluster. However, the latest CF4 data suggests that Laniakea exists within the more expansive Shapley basin of attraction, which encompasses an even greater swath of our local Universe. Among the most extraordinary revelations is the identification of the Sloan Great Wall as the largest basin of attraction discovered to date, spanning an astonishing half a billion cubic light-years—more than twice the size of the previously acknowledged Shapley basin.
A Quantum Leap in Cosmological Understanding
This monumental study not only enhances our comprehension of the gravitational web that influences cosmic structures but also significantly advances our knowledge of dark matter distribution and the dynamics of cosmic expansion. The findings pave a robust path toward refining existing cosmological models and will likely inspire future astronomical research endeavors.
As we unravel these new layers of cosmic dynamics, we gain invaluable insights into the interplay of gravitational forces that have shaped the Universe we observe today, revolutionizing our understanding of its past, present, and future. Hold on tight—our perception of the cosmos is undergoing a radical transformation!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)