
Groundbreaking AI Model Unravels the Mysteries of Gene Regulation – A New Era for Cancer Research?
2025-01-29
Author: Sarah
A revolutionary artificial intelligence model, known as EpiBERT, has been developed by an elite collaboration of experts from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Google, and Columbia University. This innovative tool predicts which genes are expressed in any type of human cell, marking a significant leap forward in genomics research that could transform our understanding of diseases, particularly cancer.
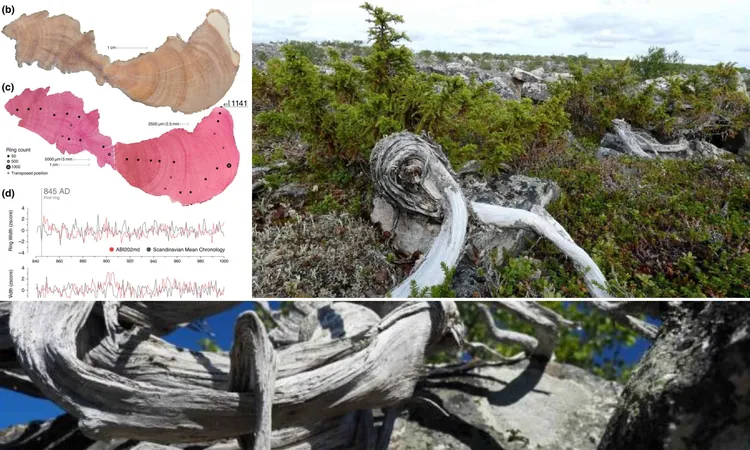
The details of this research, recently published in *Cell Genomics*, reveal that while every human cell contains the same DNA sequence, the variability between different cell types arises from the selective activation of certain genes. Approximately 20% of our genome encompasses regulatory elements that dictate gene activity, yet scientists still lack a comprehensive understanding of how these regulatory codes function, where they are located, and how mutations might disrupt their normal operation.
EpiBERT was meticulously trained on data from hundreds of human cell types, taking on the formidable challenge of analyzing the human genome, which consists of about 3 billion base pairs. By incorporating chromatin accessibility maps—indicating which portions of DNA are accessible for reading—this AI model managed to establish critical connections between the genetic sequence and gene activity in specific cell types.
The training process for EpiBERT parallels how language models like ChatGPT learn to create coherent text. Initially, it focused on understanding the relationship between DNA sequences and their accessibility, then utilized this knowledge to predict active genes in corresponding cell types. Impressively, EpiBERT can accurately identify regulatory elements that transcription factors interact with and assess their impact on gene expression across various cell types, crafting a "grammar" of genetic regulation that is both generalizable and predictable.
The implications of EpiBERT’s capabilities extend beyond fundamental research; it may enlighten scientists on how genetic regulation may go awry in diseases, particularly cancer. By unveiling the complex regulatory networks within cells, researchers could develop innovative treatments targeting these pathways. With the potential to analyze and predict gene expression in previously unseen cell types, EpiBERT may become an indispensable resource for geneticists and a crucial ally in the battle against cancer and other genetic disorders.
This transformative development in AI and genomics opens doors to unprecedented discoveries. Are we on the cusp of a medical revolution in how we understand and treat genetic diseases? Stay tuned for updates on this groundbreaking journey!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)