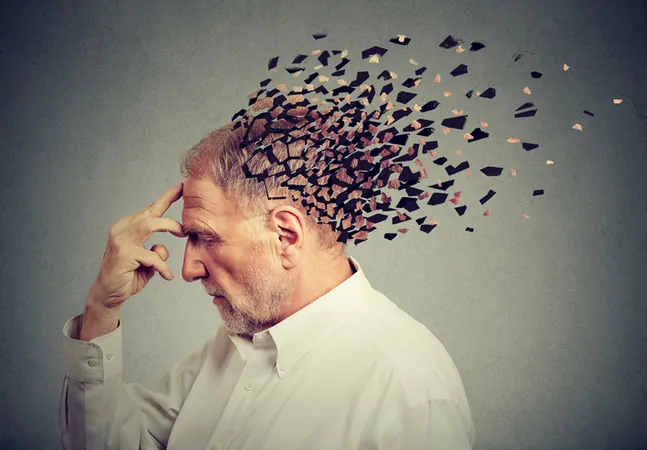

Genetic Variant Doubles Dementia Risk in Men – Shocking New Findings!
2025-06-02
Author: Sarah
A Genetic Link to Dementia Risk Revealed!
Exciting new research out of Australia has uncovered a startling connection between a common genetic variant and an increased risk of dementia in men. This study highlights that men carrying two copies of a gene variant associated with iron metabolism could see their dementia risk soar more than two-fold!
The Science Behind Iron Metabolism and Dementia
Published in the esteemed journal Neurology, this groundbreaking research focuses on the HFE gene, pivotal in regulating iron levels in the body. Mutations in this gene can lead to hemochromatosis, a genetic disorder characterized by dangerous iron buildup. Notably, two specific mutations, C282Y and H63D, have been linked to heightened dementia risk.
Study Breakdown: Who Was Assessed?
Led by Dr. John Olynyk from Curtin Medical School, the study evaluated a cohort of 12,174 individuals over the age of 70, predominantly of European descent, from a larger trial known as the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly. A significant finding surfaced: while both males and females with HFE variants showed elevated iron levels, the alarming increase in dementia risk was exclusive to men.
Men at Risk: What the Numbers Say!
Men with the H63D variant were found to have a staggering 2.39-fold higher risk of developing dementia compared to their counterparts without any HFE variants. Strikingly, this link did not hold for women, leaving researchers puzzled.
Implications for Genetic Testing
Dr. Olynyk advocates for broader testing for the HFE gene among men, especially since it’s currently routinely done in many Western countries for hemochromatosis assessment. He emphasizes that understanding this genetic predisposition could inform preventative strategies.
What Lies Ahead for Research?
Interestingly, the researchers noted that elevated iron levels did not directly correlate with increased dementia risk, opening the door to explore other underlying mechanisms – perhaps inflammatory responses or cellular damage contributing to brain injury.
A Path Forward
As research progresses, understanding the pathways influenced by the H63D variant could lead to new treatment avenues, potentially combating the damage that ultimately results in dementia. Though the genetic variant itself can't be changed, newly discovered connections could pave the way for innovative therapeutic solutions.
Stay tuned as science continues to unravel the complex relationship between genetics and dementia, uncovering new hope for prevention and treatment!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)