
Experts Warn: Could Bird Flu Evolve into a More Dangerous Threat Amidst Seasonal Flu?
2024-10-30
Author: Rajesh
Introduction
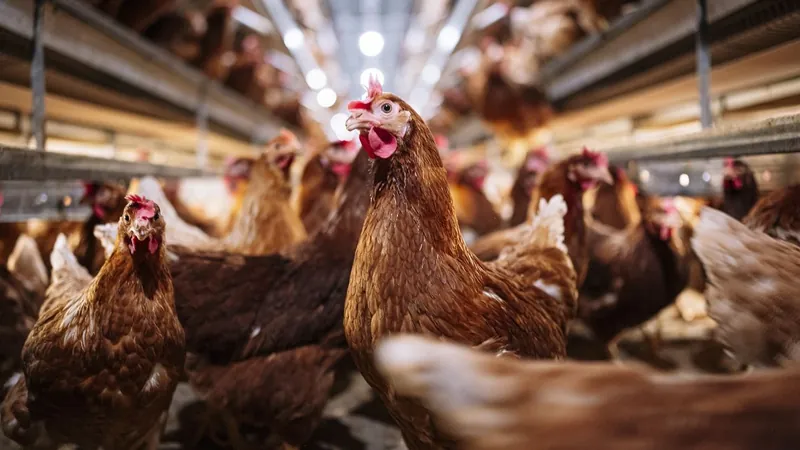
As bird flu cases continue to rise across the United States, experts are sounding the alarm about the potential for the H5N1 virus to mutate and pose a greater risk to human health. Data shows that since April 2024, there have been 36 reported human cases in 17 states, with California and Washington seeing the most infections. While nearly all cases have been linked to exposure to infected animals such as poultry, concerns are growing about the virus potentially adapting to spread among humans.
Current Situation
In the most significant week of reporting — ending on October 20 — California confirmed 16 cases, and six workers at a Washington egg farm also diagnosed with the virus raised further concerns. However, health officials have not identified any instances of human-to-human transmission thus far. Notably, a Missouri patient diagnosed in August with H5N1 caused initial fears when healthcare workers treating them exhibited symptoms, but follow-up testing showed the caregivers were free of the virus, confirming that person-to-person transmission had not occurred.
Expert Opinions
Despite the current low level of concern for the general population, experts assert that vigilance is crucial. Some scientists are warning about the possible danger of the H5N1 virus mixing with seasonal flu strains. This could lead to the emergence of a new, more virulent strain, increasing the risk of a widespread outbreak or pandemic, similar to the 2009 swine flu incident, which resulted from a similar viral reassortment process.
Strain Differences
The unique genetic makeup of the H5N1 strain currently circulating in the U.S. appears to be less aggressive than those reported in other regions, such as Cambodia, which has seen more severe cases. An immunologist noted that the Cambodian version of the virus could have mutations contributing to its increased virulence, potentially highlighting dangerous discrepancies in how different strains behave.
Testing and Surveillance
Testing capabilities for H5N1 are ongoing, focusing particularly on individuals with known exposure to infected animals. However, experts warn that as flu season ramps up, the health system may struggle to accurately diagnose and address potential H5N1 cases amid higher volumes of seasonal flu testing. Increased surveillance and testing measures are being called for, including rigorous testing protocols on farms and for farm workers.
Public Health Measures
There's a lingering question regarding whether public health measures are sufficient, given some reluctance among farmers to conduct testing due to potential impacts on productivity and costs. Recent media reports revealed a patient in Missouri who claimed no contact with infected animals, prompting speculation about possible hidden spread routes, such as contact with domestic animals or raw animal products.
Monitoring Mutations
To compound matters, ongoing mutations in the H5N1 virus pose a challenge for health agencies tasked with monitoring the virus's evolution. The CDC has had to develop new testing protocols due to mutations observed in the virus's hemagglutinin protein, which may alter test effectiveness. These developments underscore the need for a robust public health response to address potential threats from H5N1, especially as it interacts with other circulating influenza variants.
Conclusion
As bird flu cases rise, experts agree that everyone — from healthcare workers to farm operators — needs to remain alert and proactive. The stakes are high, and the world could be standing at the door of a potential health crisis if the bird flu mutates into a more dangerous form. Stay informed and vigilant as we enter another flu season.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)