
ESA's JUICE Spacecraft Confirms Earth's Habitability: A New Era for Astrobiology!
2024-09-18
Introduction
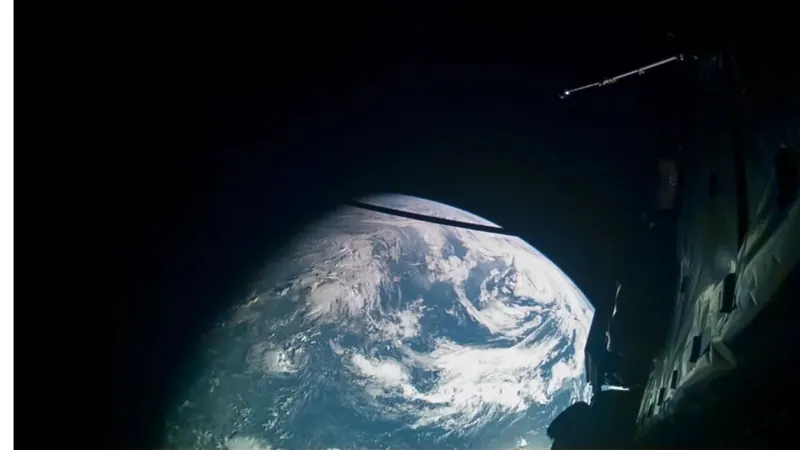
The European Space Agency’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) is on an ambitious mission to explore the mysteries of Jupiter and its fascinating moons. Launched in April 2023, JUICE recently had a brief but significant rendezvous with Earth on August 20, where it delivered some thrilling news: Earth is indeed habitable!
Key Discoveries During the Earth Flyby
During its flyby, JUICE utilized its advanced instruments to identify key elements essential for life. These included water vapor in our atmosphere, along with critical elements such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur — commonly referred to as the 'CHNOPS' elements. These findings reinforce the notion that Earth, our home, is alive with possibilities for sustaining life.
Purpose of Conducting Experiments on Earth
But why conduct these experiments on our own planet? ESA's JUICE project scientist Olivier Witasse explained, “We are obviously not surprised by these results… it would have been extremely concerning to find out that Earth was not habitable!” This test run serves a more significant purpose: ensuring the spacecraft's instruments, specifically the Moons and Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer (MAJIS) and the Submillimeter Wave Instrument (SWI), are finely tuned to operate effectively in the harsh, distant environment of Jupiter’s moons like Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa.
Exploring Jupiter's Moons
These icy moons are of particular interest because they are believed to possess subsurface oceans beneath their thick icy shells, raising tantalizing questions about the potential for life elsewhere in our solar system. Upon reaching Jupiter, JUICE will deploy the same analytical techniques to study these moons, searching for signs of habitability or even life.
Atmospheric Data Collection
In addition to confirming Earth's habitability, JUICE also gathered valuable atmospheric data including concentrations of oxygen, ozone, and carbon dioxide. Scientists plan to analyze this information, especially the levels of oxygen, and use it as a benchmark to compare with the atmospheric conditions on Jupiter's moons. This research could shed light on whether similar conditions could support biological activity, akin to what we observe on Earth.
Conclusion
While many might already assume Earth’s habitability, JUICE’s exploration serves as a crucial stepping stone in astrobiology. As we inch closer to unraveling the enigma of life in the cosmos, the insights gleaned from this mission could reshape our understanding of where, and how, life may exist beyond our planet. Buckle up — our journey towards Jupiter is only beginning!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)