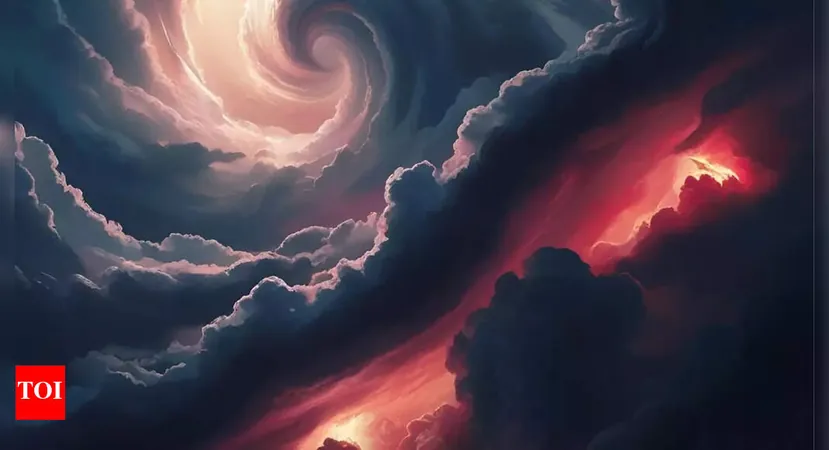

Earth's Cosmic Neighbors: The Discovery of the Enigmatic Eos Cloud
2025-05-06
Author: Jia
A Stunning Discovery in Our Cosmic Backyard
Astronomers have unveiled a breathtaking revelation: Eos, an enormous molecular cloud, is lurking just 300 light-years from Earth! Weighing in at a staggering 3,400 times the mass of the Sun, this behemoth had remained obscured for ages due to its low hydrogen content, making it nearly invisible to traditional observation methods.
The universe is a treasure trove of secrets, many undiscovered despite years of intensive research. The vastness of space continually reminds us that our knowledge is but a fraction of what lies beyond the stars. From rogue planets adrift in darkness to entire galaxies hidden behind veils of cosmic dust, the mysteries of the cosmos invite endless exploration.
Eos: The Gateway to Star and Planet Formation
The discovery of Eos opens a thrilling new chapter in understanding star and planet formation happening right in our cosmic neighborhood. This colossal molecular cloud reveals itself at the fringes of our local space, sparking immense excitement among astronomers and researchers alike.
How Was Eos Discovered?
Published in Nature Astronomy on April 28, 2025, this groundbreaking finding was made possible using data from the Korean satellite STSAT-1, equipped with a far-ultraviolet spectrograph (FIMS-SPEAR). This technology allowed astronomers to detect ultraviolet emissions from molecular hydrogen—a component that emits a glow when exposed to ultraviolet light.
Lead researcher Blakesley Burkhart from Rutgers School of Arts and Sciences expressed enthusiasm, noting, "This cloud is literally glowing in the dark. It was just waiting to be explored!" The implications of this discovery are profound, promising fresh opportunities to study the universe at a molecular level.
Why Eos is a Game-Changer in Cosmic Exploration
Eos isn't just noteworthy for its size and closeness; its massive structure sets it apart. If it were visible to the naked eye, it would span across the sky like 40 full moons in a row! Shaped like a crescent, it hovers at the boundary of a vast cavity known as the Local Bubble, which surrounds our solar system.
Understanding Molecular Clouds
Molecular clouds like Eos are stellar nurseries, primarily composed of hydrogen gas and cosmic dust—the essential ingredients for star and planet formation. These clouds are the very cradles of creation in the universe. However, many processes within them remain largely veiled in mystery.
Burkhart elaborates, "When we look through our telescopes, we witness entire solar systems forming, yet we lack detailed knowledge of how that occurs. Eos provides a unique chance to measure the formation and dissociation of these clouds and understand how galaxies transform interstellar gas and dust into stars and planets."
Eos: A Cosmic Time Capsule
Eos offers an unprecedented opportunity to observe fundamental cosmic processes as they unfold. Researchers estimate that this cloud has been forming on the edge of the Local Bubble, a gigantic 1,000-light-year-wide region of hot, low-density gas. While Eos remains stable for now, it won't endure indefinitely; scientists predict it will dissipate within the next six million years.
Most intriguingly, the materials in Eos have traversed through time for 13.6 billion years, tracing their origins back to the Big Bang. This makes Eos not only a vast structure but also a vital cosmic time capsule, composed of some of the oldest matter in existence.
Conclusion: A New Era in Cosmic Research
The discovery of Eos invites us to reconsider the wonders of our universe and the hidden marvels that lie in our cosmic backyard. As we continue to unravel these mysteries, who knows what other revelations await us just beyond the stars?




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)