Discovering New Worlds: Unraveling the Mysteries of the TOI-1266 System
2024-09-27
In a groundbreaking study, astronomers have unveiled significant insights into the TOI-1266 system, a fascinating arrangement of two temperate sub-Neptune-sized planets orbiting a nearby M dwarf star. This unique system features an unconventional architecture, where a larger planet resides in the interior orbit while a smaller one lies outside—a scenario rarely observed in planetary systems.
Researchers utilized high-precision ground-based observations alongside new data from the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) to track transit timing variations (TTVs) within the TOI-1266 system. This effort has confirmed the existence of a third, non-transiting planet, designated TOI-1266 d, which boasts a period of 32.5 days and has a mass of approximately 3.68 times that of Earth.
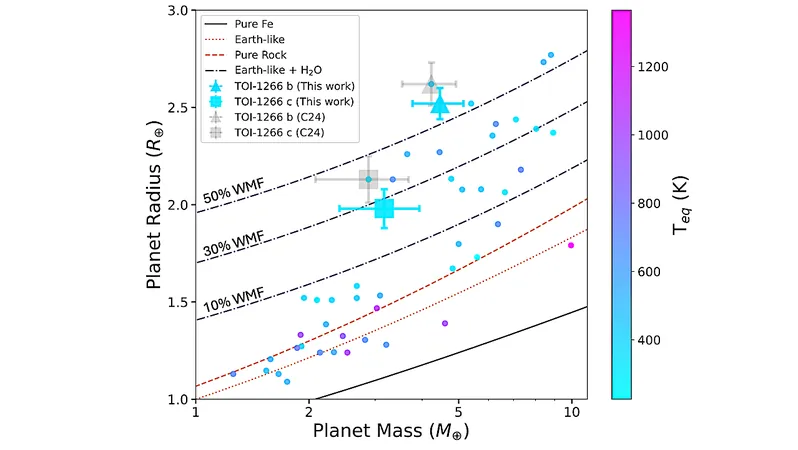
A detailed analysis revealed that TOI-1266 b—the innermost planet—measures about 2.52 times the radius of Earth with a mass of 4.46 Earth masses, exhibiting a low bulk density indicative of a hydrogen-rich envelope. Meanwhile, TOI-1266 c, the middle planet, has a radius of 1.98 Earth radii and a mass of 3.17 Earth masses, showing a higher density that may suggest either a hydrogen-rich or water-rich envelope.
The dynamic model constructed from the data illustrated that the inner and outer planets of the system are situated in a rare configuration: they are near a 3:1 period ratio while another non-resonant planet lies between them. Significantly, both TOI-1266 b and TOI-1266 d exhibit notable eccentricities, hinting that the inflated atmosphere of TOI-1266 b might be a result of tidal heating.
These revelations not only enhance our understanding of the composition and arrangement of the planets in the TOI-1266 system but also raise intriguing questions regarding their formation and future evolution. The two temperate sub-Neptunes are especially noteworthy, as they present prime candidates for atmospheric characterization with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), offering scientists an opportunity to explore the potential for habitability in planets beyond our solar system.
As we continue to uncover the complexities of distant worlds, the TOI-1266 system stands out as a remarkable benchmark in the study of exoplanets, paving the way for further discoveries and deeper insights into the architecture of our universe. Stay tuned for more exciting updates in the field of planetary science!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)