
Discovering Antarctica's Mysterious Snow Dunes: A Game-Changer for Climate Research!
2024-10-01
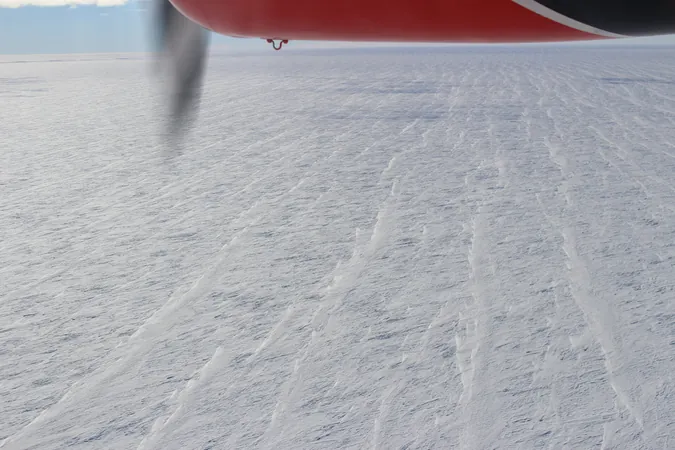
In the vast and icy expanse of Antarctica, a surprising geological feature is reshaping our understanding of one of the harshest environments on Earth. While sand dunes are commonly associated with deserts and beaches, scientists have now turned their attention to the enigmatic dunes formed by snow. A groundbreaking study has unveiled the intricate dynamics of these snow formations and their implications for understanding climate patterns across the continent.
Antarctica's Unexpected Geological Feature
Antarctica, recognized as the largest desert globally, is not only a barren, snow-covered wilderness but also home to remarkable snow dunes. Unlike their sandy cousins, these structures are meticulously shaped by the interplay of wind and the unique properties of snow. Some of the snow dunes can stretch over several kilometers in length, though they remain comparatively low, often just several dozen centimeters high, unlike towering sand dunes.
Documenting the Snow Dunes
Despite their presence, many of Antarctica's snow dunes have gone largely undocumented, overshadowed by smaller formations and massive megadunes mapped through remote sensing technologies. The recent study, led by researchers from Université Grenoble Alpes and the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris, employed advanced satellite data from the Copernicus Sentinel-2 program to shed light on these elusive snow dunes.
Research Findings
Examining more than 33,000 satellite images collected between 2018 and 2021, the team studied a staggering 7.5 million square kilometers—approximately 60% of the Antarctic continent. The findings highlight that the formation of these dunes is primarily governed by wind-driven snow transport, with an intriguing twist: the process known as snow sintering plays a pivotal role. This phenomenon involves the thawing and refreezing of snow particles, ultimately leading to a slowed movement, which permits the elongation of snow dunes without significant height accumulation like traditional sand dunes.
The Discovery of Longitudinal Dunes
A striking revelation from the study is the dominance of longitudinal dunes, which make up a whopping 61% of observed formations. These elongated shapes emerge where persistent, unidirectional winds prevail, particularly in East Antarctica, where they align with winds streaming from the high interior towards coastal areas. This discovery implies a concerning limit on snow availability, suggesting that even in regions with high snowfall, strong winds often redistribute snow before it accumulates sufficiently.
Implications for Climate Research
The implications of understanding these snow dunes extend far beyond geographical curiosities. They hold the key to unlocking secrets about Antarctica's surface mass balance—essential for gauging climate changes. With snow sintering controlling the movement of snow, the evidence suggests that more snow could be resting on the surface than previously recognized. This insight is crucial for predicting how Antarctica's ice mass might respond to climate change.
Future Monitoring of Antarctica
As global temperatures rise, the intricate balance of snow accumulation, wind intensity, and temperature could be set for dramatic shifts. The potential evolution of snow dunes in a warmer and windier future may fundamentally alter the patterns of snow distribution across the continent.
Technological Advancements in Research
This pivotal research would not have been possible without the enhanced observational power provided by the Sentinel-2 satellites. Their high-resolution imagery revealed snow dunes extending beyond 20 meters, offering unprecedented insights into Antarctica's complex surface morphology.
The Role of Sentinel-2C
Moreover, with the recent launch of the Sentinel-2C satellite, researchers can expect even more frequent and detailed observations. This advancement reinforces the ongoing significance of the Copernicus program in environmental monitoring and helps scientists better predict the continent's future under changing climatic conditions.
Conclusion
As we strive to unlock the secrets of Antarctica’s frozen landscape, this groundbreaking study serves as a reminder that beneath the snow lies a world of discovery with far-reaching implications for our climate and environment. What mysteries will be revealed next in this frozen frontier? Stay tuned!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)