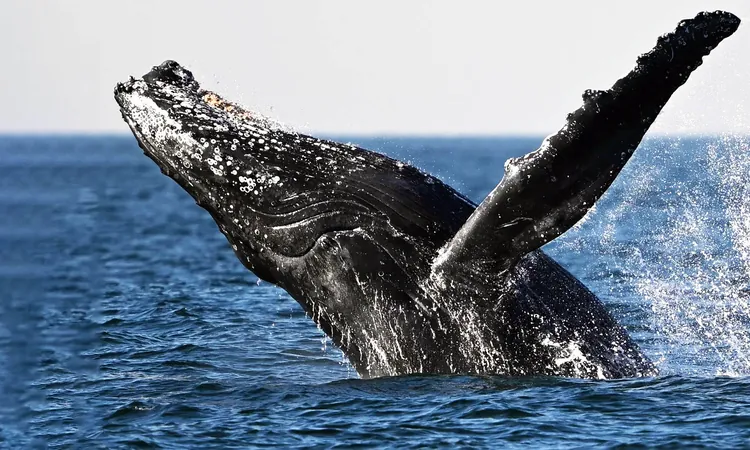

Discover the Majestic Underwater World of Gray Whales: Bubble Rings and Headstands!
2024-09-26
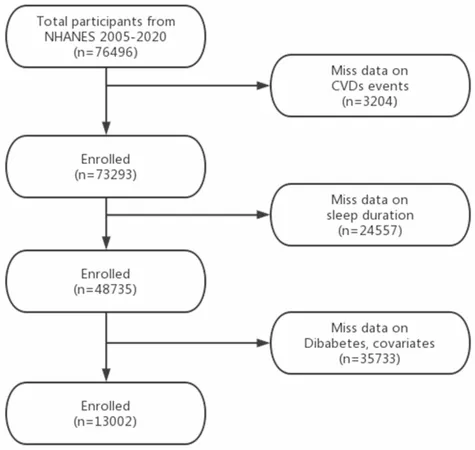
Recent advancements in drone technology have allowed researchers to delve into the captivating foraging behaviors of gray whales off the gorgeous Oregon coast. Clara Bird, a dedicated researcher at Oregon State University, has accumulated an impressive seven years of drone footage revealing remarkable insights into the lives of these magnificent marine mammals.
Unraveling Whale Behaviors
Bird's extensive studies have unveiled how age and size significantly affect gray whales’ foraging tactics. She discovered that younger, smaller whales tend to swim straightforwardly while foraging, whereas their older and larger relatives exhibit a curious behavior known as “headstanding.” This unique move involves whales diving headfirst into the ocean floor, resembling a human handstand! This behavior is not just an eccentric display—it signals strength and skill acquired through experience.
“Watching young whales attempting to mimic their elders and struggling in headstands is a remarkable spectacle. It adds a layer of awe to their growing process,” Bird remarked.
Feast for the Giants
Beyond the astonishing headstands, Bird and her colleague, Associate Professor Leigh Torres, also noted that gray whales adapt their foraging strategies depending on their environment. Notably, these magnificent creatures are more likely to perform headstands around reefs—home to their favored treat, mysid shrimp.
Bubbles for Buoyancy: A New Discovery
Adding to the mesmerizing behaviors of gray whales is the phenomenon of “bubble blasts.” This striking behavior occurs when a whale forcefully exhales underwater, creating eye-catching circular patterns on the ocean's surface. Initially thought to assist in capturing prey, new findings suggest these bubble blasts serve to help regulate buoyancy during foraging in shallow waters.
Larger whales, particularly those with more body mass, tend to utilize bubble blasts extensively, especially during headstands. This adaptation allows them to dive deeper and feed for longer periods, ensuring they can take full advantage of their feeding grounds.
Social Structures and Interactions
Bird's research goes beyond individual foraging habits—it also sheds light on the intricate social interactions among gray whales. Often spotted in small groups, these whales exhibit synchronized swimming and cooperative foraging behaviors, suggesting a sophisticated level of communication and social intelligence within their communities.
Understanding these social dynamics provides crucial insights into the relationships that develop among gray whales, which can directly influence their survival and efficiency during feeding.
Conservation Efforts Inspired by Research
The wealth of knowledge gained from these observations isn't just of academic interest; it plays a fundamental role in shaping conservation strategies for gray whales. By pinpointing critical feeding areas—like kelp-rich reefs—scientists can advocate for the protection of these habitats against human encroachment and pollution.
A Call to Action
With every revelation about gray whales, we are reminded of the wonders of the ocean and the vital roles these creatures play within our ecosystem. Their behaviors not only fascinate us but also emphasize the importance of safeguarding their habitats.
The study detailing these groundbreaking findings has been published in the journal *Animal Behaviour*, further enriching our understanding of marine life.
As we continuously uncover the secrets of the ocean's depths, let us commit ourselves to protect these elegant giants and their ecosystems. Their lives pave the way for preserving the beauty of our planet's underwater world.
Curious to learn more about these extraordinary creatures? Stay tuned for further updates and insights into marine conservation!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)