Discover How a Gut Protozoan Influences Lung Health and Respiratory Diseases Like Never Before!
2024-12-22
Author: Siti
A Groundbreaking Discovery
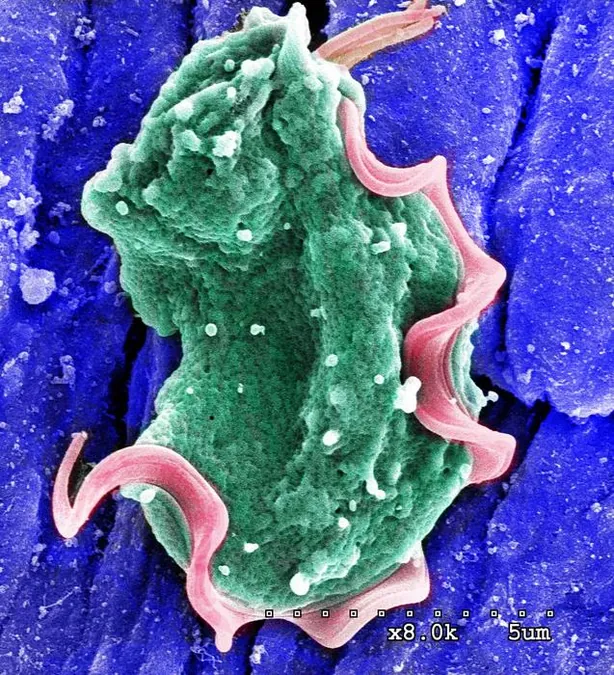
In an astonishing breakthrough, recent research uncovers the profound impact that microbes residing in our gastrointestinal tract—including a specific protozoan—have on our lung health and immune function. As we navigate the complexities of the human microbiome, a groundbreaking study published in Cell highlights how a gut protozoan called Tritrichomonas musculis can significantly influence respiratory diseases.
The Role of Gut Microbes
Gut microbes, numbering in the trillions, play crucial roles in digestion and nutrient absorption, but their influence extends far beyond the intestines. "These peaceful microbes are pivotal players in modulating our immune system," explains Arthur Mortha, an associate professor at the University of Toronto. "Our research aims to delve deeper into how these microorganisms affect diseases in various organs including the lungs, brain, skin, and joints."
The Unexplored Potential of Protozoa
While much is known about gut bacteria and their health effects, protozoa—more complex single-celled organisms—have remained underexplored. Some of these protozoa are known as parasites, while others, like T. musculis, can live in symbiosis with their host.
Research Findings
In the study, researchers utilized a mouse model to analyze the effects of T. mu on lung immune cells. Remarkably, the presence of this protozoan correlated with elevated levels of specific immune cells within the lungs. Tracking their journey, it was discovered that many of these immune cells migrated from the gut to the lungs, where they played a crucial role in managing the lung's immune response and changing the outcome of respiratory infections.
The Dual Nature of T. musculis
Mortha likened T. mu to a conductor, orchestrating immune functions across different body systems. However, the repercussions of T. mu's presence are complex: while it may bolster defenses against respiratory infections, it might also exacerbate conditions such as allergic asthma.
Implications for Health
The dual nature of this protozoan highlights the intricate balance of the immune system. Mortha expressed concerns that T. mu could worsen inflammatory bowel diseases and potentially increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Yet, intriguingly, it also enhances the host's capacity to battle severe infections.
Looking Ahead
Further research examining sputum samples from individuals suffering from severe asthma revealed higher concentrations of certain protozoa associated with these patients. This could mean significant implications for human health, suggesting that our findings in mouse models might extend to people.
As scientists delve deeper into the role of the gut microbiome, this study opens up new avenues for understanding respiratory conditions and may eventually guide the development of innovative diagnostic and treatment strategies for individuals grappling with respiratory and inflammatory disorders.
Stay tuned, as this research is set to unravel new ways to optimize gut health for better overall well-being and respiratory outcomes!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)