Critical Insights into Obstetric Outcomes of Breastfeeding Women Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
2025-01-11
Author: Wei Ling
Introduction
Breastfeeding is a cornerstone of maternal and infant health, significantly reducing morbidity and mortality rates in newborns both in the short and long term. Yet, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented unprecedented challenges to maternal health services and breastfeeding practices worldwide.
Study Objectives
This research investigates and contrasts obstetric outcomes in women who breastfed immediately after delivery against those who did not, specifically examining the pre-pandemic and pandemic periods.
Research Methodology
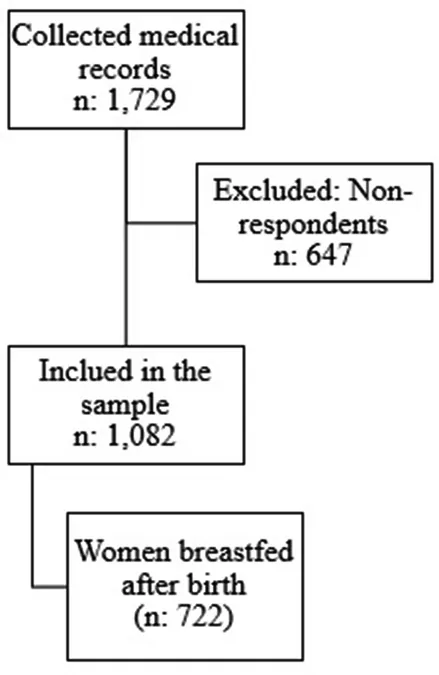
Conducted as a cross-sectional epidemiological study nested within a cohort, the investigation utilized secondary data from the 2020 Brazilian survey “Birth and Breastfeeding in Children of Mothers Infected with SARS-CoV-2.” This data was juxtaposed with that of a similar study, “Birth in Belo Horizonte," conducted from 2011 to 2012, forming a comprehensive view of changes in maternal health behavior over a decade.
Study Results
The findings incorporated data from 1,082 women during the COVID-19 wave and 382 from the pre-pandemic era. Notably, a higher percentage of women who breastfed within the first hour post-delivery in the pre-pandemic group did not undergo cesarean delivery and exhibited fewer obstetric complications than their pandemic counterparts.
Comparative scrutiny of infected/suspected versus non-infected women revealed that non-infected mothers had more favorable delivery rates and greater breastfeeding success shortly after birth. Moreover, multivariate analyses revealed critical insights: women with fewer than seven prenatal visits were 36% less likely to initiate breastfeeding, while those who underwent cesarean sections had a 61% reduced probability of breastfeeding after delivery.
Key Findings and Insights
1. **Prenatal Care's Role:** Enhanced prenatal monitoring is essential to empower women to breastfeed successfully post-delivery, especially during health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. Historical data shows that women engaged in extensive prenatal care were significantly more likely to breastfeed.
2. **Impact of Cesarean Sections:** Cesarean deliveries were shown to have a detrimental effect on the likelihood of breastfeeding shortly after birth. Women who had cesareans had markedly lower breastfeeding initiation compared to those who had vaginal births.
3. **Need for Supportive Practices:** The study underscores that immediate breastfeeding and skin-to-skin contact are critical for establishing the mother-infant bond and improving breastfeeding rates. However, pandemic-induced policies created barriers to these practices, negatively impacting maternal-infant outcomes.
4. **Global Health Recommendations:** International agencies like WHO have recommended maintaining breastfeeding regardless of maternal COVID-19 status, citing the critical immunological benefits of breast milk. Yet, the pandemic necessitated complex health protocols that often limited mothers' abilities to engage in recommended practices.
Conclusion
In summary, the pandemic has significantly disrupted breastfeeding practices, highlighting the need for urgent overhaul in healthcare strategies. As we adapt to the ongoing realities of COVID-19, it is vital that maternal health policies prioritize women's autonomy and foster inclusive environments that support breastfeeding.
The ripple effects of the pandemic on maternal health call for continued research and adaptations in health systems globally, with an emphasis on equitable access to prenatal care and supportive maternal practices. Stakeholders in maternal health must harness these findings to inform future policies and guidelines, ensuring that every newborn has the opportunity for a healthy start to life through breastfeeding.
Call to Action
Healthcare professionals, policymakers, and communities must unite to advocate for mothers and establish supportive environments to counteract the setbacks in maternal and child health, paving the way for resilient health systems amid challenges like a pandemic.
Don't Miss the Latest Updates!
For more comprehensive insights and health guidelines, stay tuned to our upcoming articles exploring the impacts of COVID-19 on maternal health and sharing success stories from mothers worldwide!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)