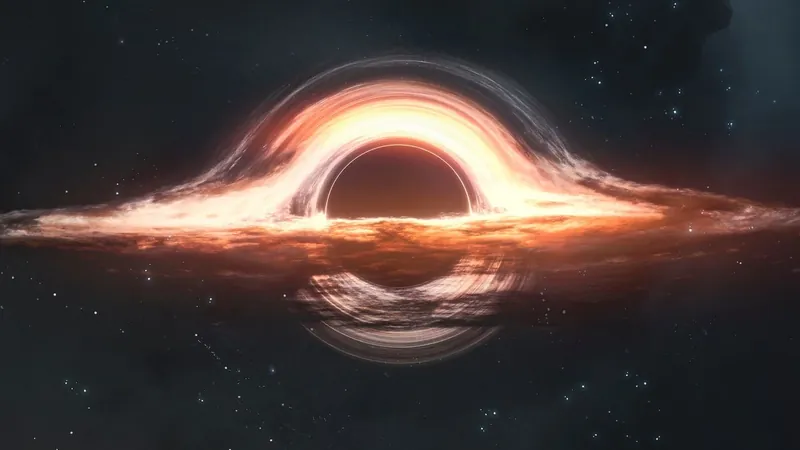

Could Black Holes Be the Hidden Catalysts Behind the Universe's Expansion?
2024-10-31
Author: Daniel
Groundbreaking Study Links Black Holes to Dark Energy
A groundbreaking study suggests that black holes might play a pivotal role in the mysterious phenomenon of dark energy, which is accelerating the expansion of our universe. Dark energy, a perplexing force that constitutes about 70% of the cosmos, is believed to have originated from the aftermath of the Big Bang, which occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
The Mystery of Dark Energy
The origin of dark energy has puzzled scientists for decades. While many theories have been proposed, including the idea that it exists uniformly across space, a newer hypothesis suggests that it could actually be derived from the cores of massive black holes. Previously dismissed by some as outlandish, this theory has now gained traction following recent findings.
Recent Findings on Black Holes and Dark Energy
In a study published on October 28 in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, researchers uncovered compelling evidence linking the growth of black holes with the increasing density of dark energy. They assert that as the universe ages and black holes accumulate mass, the dark energy density also rises, suggesting a potential interrelation between these two cosmic giants.
Questions Raised by Researchers
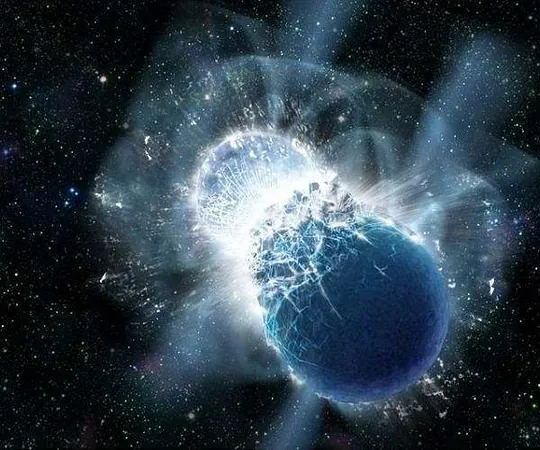
Gregory Tarlé, a co-author of the study and professor of physics at the University of Michigan, posed an intriguing question: "Where in the later universe do we see gravity as strong as it was at the beginning?" He pointed to black holes, asserting that they might serve as the cosmic backbones for the energy dynamics of the universe. Tarlé speculated that the gravitational collapse of a massive star may transform its matter into dark energy, hinting at a striking reversal of the conditions that occurred during the universe's inflationary phase—almost like a mini Big Bang occurring in reverse.
The Research Methodology
To investigate this hypothesis, the research team utilized the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) on the Nicholas U. Mayall Telescope in Arizona. This powerful tool allows astronomers to track the positions of millions of galaxies, facilitating an analysis of the universe's expansion history. By examining the relationship between black hole mass growth and dark energy density at various cosmic epochs, the researchers made a fascinating observation—the two phenomena appeared to correlate, strengthening the proposition that black holes could indeed be a source of dark energy.
Significant Breakthrough in Understanding the Universe
Duncan Farrah, another co-author and an associate professor of physics at the University of Hawaii, highlighted that as massive stars perish and new black holes form, dark energy levels in the universe seem to increase correspondingly. This unexpected alignment could represent a significant breakthrough in understanding the universe's expansion.
Implications for Cosmology
The implications of this research are far-reaching, particularly as they relate to an ongoing puzzle in cosmology known as the "Hubble tension." This dilemma arises from conflicting measurements of the universe's expansion rate, which threaten to unravel our current understanding of cosmological theories.
The Path Forward
While the connection between black holes and dark energy is intriguing, the authors caution that more observational data—both from DESI and other experiments—are necessary to draw definitive conclusions. As Tarlé emphasized, the question of whether black holes contribute to dark energy has transitioned from a theoretical discussion to an experimental challenge.
Conclusion
As astronomers and physicists dive deeper into the cosmos, they stand on the brink of potentially revolutionizing our understanding of the universe. Are black holes the secret architects behind dark energy? Only time and further research will tell. Buckle up for a thrilling journey into the unknown!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)