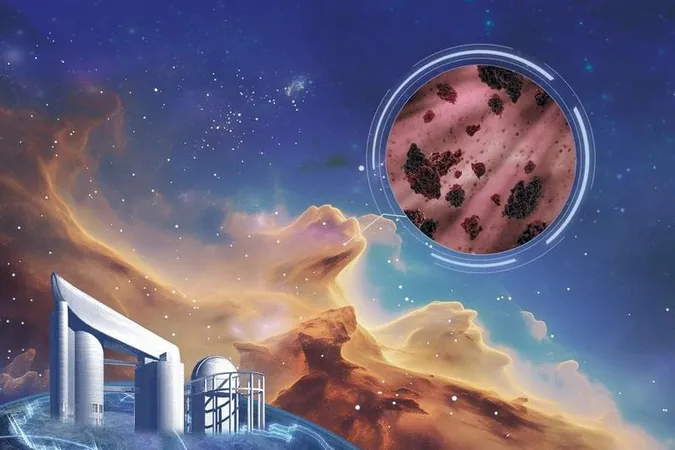

Cosmic Breakthrough: 3D Map of Interstellar Dust Unveiled!
2025-03-15
Author: Jia
Introduction
In an astounding collaboration, astronomers from China and the United States have successfully created the first-ever three-dimensional map of interstellar dust in our Milky Way galaxy. This monumental achievement was made possible through data collected from China's Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopy Telescope (LAMOST) and the European Space Agency’s Gaia space observatory.
Significance of the Study
This groundbreaking study was published as the cover story in Science and addresses a long-standing question in astronomy: how interstellar dust dims and reddens the light from stars scattered across the galaxy. The findings are set to transform the fields of star formation, the study of exoplanets, and even offer insights into the very origins of life itself.
Expert Insights
Zhang Xiangyu, a PhD student at the Max Planck Institute in Germany, highlighted the significance of interstellar dust, describing it as “cosmic fog” that absorbs and scatters starlight—a phenomenon known as extinction. Until now, astronomers struggled with simplifying models that treated dust uniformly, akin to using a flawed GPS for navigation.
A Revolutionary Methodology
“This new approach is like upgrading from black-and-white TV to a 3D IMAX experience for dust studies,” Zhang explained, emphasizing that the properties of dust vary widely across different regions of space. The research team, including Zhang and his advisor Gregory M. Green, overcame this limitation by combining an impressive 2 million stellar spectra from LAMOST with data from the Gaia observatory.
Dynamic 3D Map
The result? A dynamic 3D map that illustrates how dust extinction varies by both location and wavelength. This map extends an astonishing 16,000 light years deep into the galaxy's structure and reveals significant variations in dust properties over that vast expanse.
New Insights
Zhang stated, "For the first time, we can see the Milky Way's dust 'fingerprints' in full dimensionality." This leap forward provides a richer context for astrochemistry and star formation, suggesting a potential new understanding of how life’s building blocks are formed and distributed throughout the cosmos.
Future Prospects
As the research team continues to utilize LAMOST’s ongoing surveys, they aim to further enhance this map, investigating how the evolution of dust might be linked to the broader history of our galaxy. With these advancements, the potential to unlock secrets of the universe is greater than ever.
Conclusion
Stay tuned—this cosmic journey has only just begun, and the revelations may change everything we know about our galaxy and the origins of life!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)