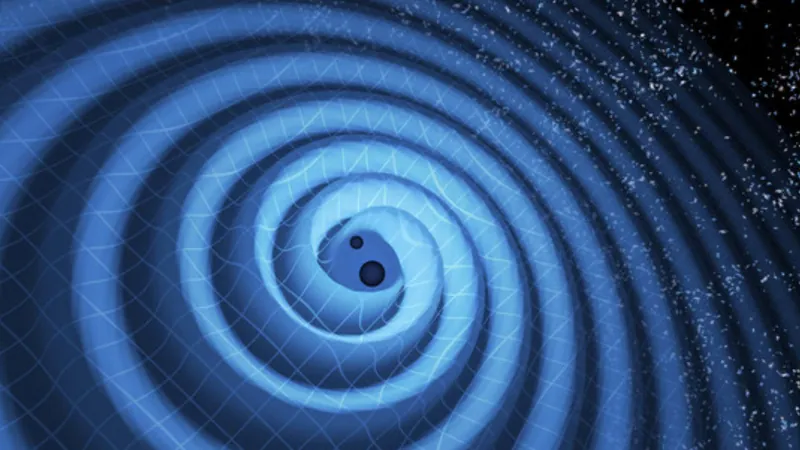

Celebrating LIGO’s Legacy: 10 Groundbreaking Gravitational Wave Discoveries Since 2015
2025-09-14
Author: Jia
September 14, 2015, marked a monumental day in scientific history as the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) made the first-ever detection of gravitational waves—tiny ripples in space-time—caused by the merger of two black holes. This unprecedented achievement confirmed Albert Einstein's century-old predictions about the nature of gravity.
The Rise of Gravitational Wave Astronomy
Since LIGO's groundbreaking discovery, which also highlighted the collaboration with the Virgo observatory in Italy and KAGRA in Japan, the field of gravitational wave astronomy has boomed. The instruments have been refined to detect distortions smaller than a proton’s size, leading to over 300 gravitational wave signals, a new frontier for understanding violent cosmic events.
1. Einstein’s Hypothesis Confirmed: The Historic Detection of GW150914
The gravitational wave signal GW150914, detected on September 14, 2015, was generated from the merger of two black holes, each about 30 times the mass of the sun. This discovery not only validated Einstein's theory of general relativity but also provided strong evidence that black hole mergers are indeed a cosmic reality.
2. The Most Massive Black Hole Merger Yet!
On November 23, 2023, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration detected GW231123, an extraordinary merger between black holes weighing 100 and 140 solar masses. This event shattered records, leading to a daughter black hole approximately 225 solar masses, challenging our existing models of black hole formation.
3. A Golden Discovery: Neutron Star Merger GW170817
August 17, 2017, saw the discovery of GW170817, the first gravitational wave event from a neutron star collision, located 130 million light-years away. This monumental event allowed scientists to explore the origins of heavy elements like gold and silver, marking a significant milestone in nuclear physics.
4. Enter Multimessenger Astronomy!
GW170817 didn’t just make waves in the gravitational realm; it also illuminated the electromagnetic spectrum through the phenomenon known as a kilonova. This event marked the birth of multimessenger astronomy, enabling researchers to observe cosmic events via multiple channels, enriching our understanding of the universe.
5. The Ringing Toll of Gravitational Waves
As binary black holes spiral together, they emit a unique ringdown signal resembling a bell's tone, detected in events like GW190521. This phenomenon has led to unprecedented insights into black hole properties and provides evidence for Einstein’s theories standing strong against extensive scrutiny.
6. The Sweet Spot: Mixed Merger Discovery!
On January 5, 2020, LIGO/Virgo detected a neutron star-black hole merger, GW200105_162426. Labelled a "mixed merger", this event opened a new chapter, shedding light on the dynamics of these elusive cosmic pairings.
7. The Lightest Black Hole Mystery!
On August 14, 2019, GW190814 captivated astronomers with its intriguing nature: combining a murky object, possibly the lightest black hole or heaviest neutron star ever recorded, challenging our perceptions of stellar remnants.
8. The Loudest Signal Ever Recorded!
Fast forward to September 10, 2025, when the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA team announced the detection of GW250114. This event stood out not just for its clarity but also for breaking new ground in testing the predictions of general relativity.
9. A Cosmic Symphony: NANOGrav’s Discovery!
In a non-LVK revelation, June 28, 2023, marked a significant success for NANOGrav, which detected low-frequency gravitational waves—an exploration into the faint harmonies produced by supermassive black holes swirling in the depths of space.
10. The Irony of Einstein’s Predictions
While gravitational wave discoveries have continuously affirmed Einstein's theories, they ironically prove him wrong about their detectable nature. Some renowned physicists initially doubted that gravitational waves would ever be observable, ironically highlighting the monumental strides made by modern science.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)