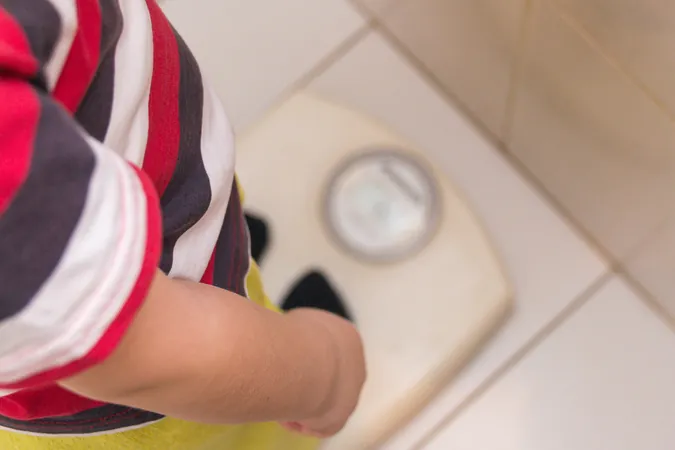

Cancer Deaths Linked to Obesity Soar: Alarming Disparities Uncovered
2025-07-14
Author: Yu
Obesity-Related Cancer Deaths Surge: A Grim Trend
A shocking new report reveals that obesity-related cancer deaths in the U.S. have skyrocketed threefold over the last two decades. This distressing trend, unveiled at the ENDO 2025 conference, highlights stark disparities based on gender, race, age, and geographic location.
Who is Most Affected?
The data paints a troubling picture, particularly among older adults, rural inhabitants, and those in the Midwest. Women and racial minorities are feeling the brunt of these alarming statistics.
Dr. Faizan Ahmed, the lead researcher from Hackensack Meridian Jersey Shore University Medical Center, states, "Obesity is a crucial contributor to various cancers, leading to significant mortality rates. Our findings emphasize the urgency for targeted public health initiatives, including early screenings and greater access to healthcare in high-risk and underserved areas."
Inside the Study: Key Insights and Findings
The study, building on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), pinpointed 13 types of cancer linked to obesity. These include esophageal adenocarcinoma, colorectal cancer, and postmenopausal breast cancer, among others.
Analyzing over 33,000 obesity-associated cancer deaths from 1999 to 2020, researchers uncovered a stark increase in mortality rates, which rose from 3.73 per million in 1999 to a staggering 13.52 in 2020.
Shocking Statistics
The average annual increase in mortality stood at nearly 6%, but the most alarming spike occurred between 2018 and 2020, with an average annual change of over 19%. Women experienced a mortality rate of 7.22, while men had a slightly lower rate of 6.59, reflecting ongoing gender disparities.
Disparities also emerged along racial lines, with Hispanic individuals exhibiting the most drastic annual percent change in mortality at 6.31%, while Black individuals recorded a lower increase.
The Age Factor
Age plays a significant role, particularly as those aged 65 and older faced a staggering mortality rate of 41.54 by 2020.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)