Can Ozone Uncover Life Beyond Earth? The Surprising Role of Methane in Oxygen Detection!
2025-08-29
Author: John Tan
As scientists continue to hunt for signs of life across the cosmos, they've identified molecular oxygen (O2) paired with methane (CH4) as a beacon of potential biological activity. This intriguing duo suggests a unique chemical imbalance that could hint at life.
However, there are scenarios where detecting O2 directly may be challenging, such as in poorly lit environments or in atmospheres with sparse oxygen levels. Enter ozone (O3), the byproduct of O2, which researchers propose could serve as a stand-in to gauge O2 abundance.
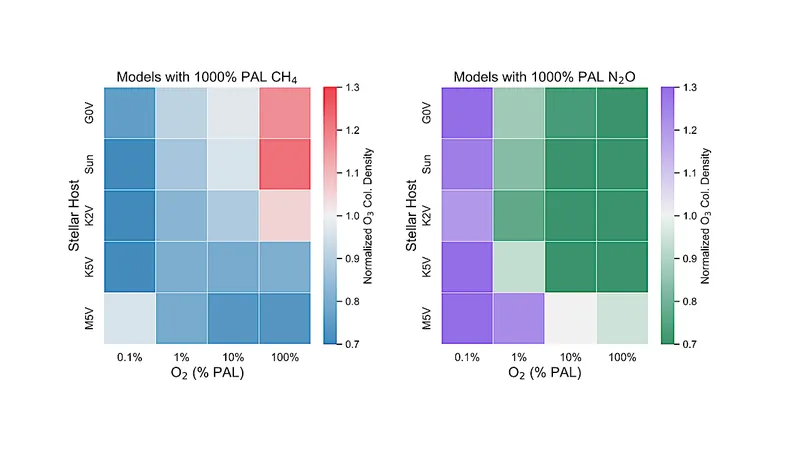
This article dives into a comprehensive study that investigates the complex relationship between O2 and O3 under varying celestial and atmospheric conditions. By simulating Earth-like planets across different O2 levels—ranging from 0.01% to a staggering 150%—and manipulating methane concentrations (from 10% to 1000% of present atmospheric levels), scientists aim to unveil the nuances of this interaction.
Methane isn't just a solo act; it plays a pivotal role as a potential biosignature and a source of hydrogen atoms that can break down O3. This dynamic interaction raises significant questions about how methane influences ozone levels and, consequently, the detection of oxygen.
Notable findings indicate that varying levels of CH4 substantially alter the O2-O3 dynamics—particularly in regions orbiting hotter stars. In these high O2 environments, a considerable amount of methane transforms into water vapor, altering stratospheric temperatures and impacting the rates at which ozone forms and disintegrates.
Additionally, shifts in hydroxy (HOx) compounds influence not only ozone production but also the ultraviolet (UV) radiation penetrating the atmosphere, along with variations in the ozone spectral feature. These discoveries underscore the importance of grasping the O2-O3 correlation if we aim to employ ozone as a reliable indicator for oxygen in future extraterrestrial explorations.
This research sets the stage for a groundbreaking exploration of biosignatures beyond our planet, paving the way for future discoveries in the search for life in the Universe.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)