Breakthrough Study Sheds Light on NUT Carcinoma: The Hidden Threat and How to Detect It!
2025-07-24
Author: Arjun
Revealing the Dark Truth About NUT Carcinoma
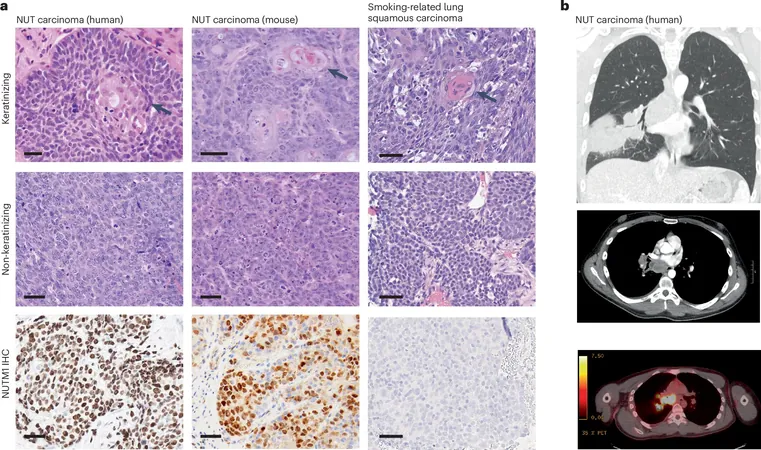
A groundbreaking study from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute has unveiled alarming insights into NUT carcinoma, a rare and aggressive form of cancer affecting the lungs, head, and neck. This research highlights a disturbing potential for underdiagnosis, emphasizing the crucial need for enhanced testing methods.
Why Standard Tests Are Failing Patients
According to the findings published in *Clinical Cancer Research*, the standard DNA tests currently used to identify cancer may miss over 75% of NUT carcinoma cases. These tests are not equipped to detect the specific gene fusions that are crucial indicators of this disease.
The Essential Tests You Need to Know
To accurately diagnose NUT carcinoma, clinicians must utilize advanced testing techniques. These include NUT immunohistochemistry (IHC), RNA fusion testing, and NUTM1 FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) — tests that have demonstrated a much higher success rate in identifying the disease.
A Message from Experts: Change is Urgent!
Dr. Jia Luo, a leading thoracic oncologist at Dana-Farber, urged healthcare providers, saying, "If NUT carcinoma is suspected, relying on standard DNA testing alone is simply not enough. Clinicians need to seek out specialized tests to ensure timely and accurate diagnoses, which can be pivotal for patient outcomes and treatment options."
Understanding NUT Carcinoma: A Closer Look at its Aggressiveness
NUT carcinoma stands out as a particularly vicious form of squamous cell cancer, often affecting younger individuals with limited or no smoking history. Disturbingly, patients diagnosed with this form of cancer face a bleak median survival rate of just 6.7 months.
The Science Behind NUT Carcinoma: What Makes It Unique?
At the core of NUT carcinoma are fusions involving the NUTM1 gene, which occur due to genomic errors linking two genes together, leading to the production of dysfunctional proteins. The study analyzed 116 tumors, revealing that standard tests only detected these fusions in less than 25% of cases.
A Call for Immediate Action in Diagnostics
In a striking contrast, NUT IHC, RNA fusion tests, and NUTM1 FISH boasted detection rates of 100%, 84%, and 92%, respectively. Dr. Luo emphasized the necessity for a shift in diagnostic protocols: "Our findings demand immediate changes in how suspected NUT carcinoma cases are managed."
Exploring Further: Are There Other Mutations?
Alongside the primary focus on NUT fusions, the researchers also cataloged other mutations found in these cancer cases. While some tumors did not present any additional mutations, others showcased changes in genes tied to epigenetics and DNA repair pathways.
The Future of Treatment: Hope on the Horizon
As they move forward, Luo and his team plan to conduct laboratory studies aimed at exploiting these additional mutations for new treatment options. "Understanding the common mutations associated with NUT carcinoma is a crucial step in developing effective combination therapies in the future," he concluded.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)