Breakthrough Laser Technology Sets New Standard for Stent Surgery
2024-12-26
Author: Nur
Groundbreaking Advancement in Cardiovascular Health
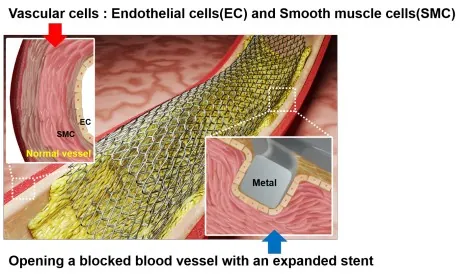
In a groundbreaking advancement for cardiovascular health, a dedicated research team led by Dr. Hojeong Jeon and Dr. Hyung-Seop Han from the Biomaterials Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) has developed a revolutionary stent surface treatment technology. Utilizing cutting-edge laser patterning, this innovative method not only encourages the growth of endothelial cells but also inhibits the problematic dedifferentiation of smooth muscle cells in blood vessels. This dual approach is set to significantly enhance vascular recovery, particularly when paired with existing chemical coating techniques.
The Importance of Therapeutic Stents
As South Korea transitions into a super-aged society, the prevalence of vascular diseases among its aging population is escalating. The importance of therapeutic stents, which are crucial for maintaining blood flow by widening narrowed or blocked blood vessels, has never been more vital. However, traditional metal stents often lead to a condition known as restenosis, where arteries can re-narrow due to a proliferation of smooth muscle cells just a month post-implantation.
Addressing Restenosis with New Approaches
To combat this issue, drug-eluting stents have been commonly employed, but they frequently hinder the process of vascular re-endothelialization, which increases the risk of thrombosis and the need for anticoagulants. Researchers have long sought to enhance stent surface coatings with bioactive molecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, although these coatings generally fail to adequately boost endothelial cell proliferation.
The Breakthrough in Laser Texturing Technology
The breakthrough achieved by Dr. Jeon and his team involves applying advanced nanosecond laser texturing technology to create micro- and nano-scale wrinkle patterns on nickel-titanium alloy stents. These intricate patterns effectively inhibit the migration and morphological changes of smooth muscle cells resulting from stent-induced vascular injury, thereby preventing the occurrence of restenosis. Furthermore, the enhanced cellular adhesion from the wrinkle patterns promotes efficient re-endothelialization, aiding in the restoration of the vascular lining.
Validation Studies and Results
Initial validation studies conducted in vitro and ex vivo using fetal animal bones demonstrated the effectiveness of this new laser texturing technology. It was shown to foster a favorable environment for endothelial cell proliferation, while simultaneously suppressing the excessive growth of smooth muscle cells—growth on the textured surfaces was reduced by an impressive 75%, while angiogenesis was increased by more than twofold.
Implications for Biodegradable Stents
Promisingly, this surface patterning technology is expected to extend its benefits beyond conventional metal stents and into biodegradable stents. The incorporation of these patterns could prevent restenosis and enhance endothelialization even before the biodegradable stents dissolve, ultimately improving patient outcomes and minimizing complication risks. The research team is now preparing for animal testing and clinical trials to further assess the long-term safety and efficacy of this innovative laser patterning technology.
Expert Insights and Future Directions
Dr. Jeon remarked, “This study showcases the potential of surface patterns to selectively regulate vascular cell responses without the need for drugs. The use of widely available nanosecond lasers allows for precise and rapid processing of stent surfaces, presenting significant advantages for commercialization and manufacturing efficiency.”
Conclusion: A Hope for Safer Cardiovascular Treatment
As cardiovascular diseases continue to rise, particularly in aging populations, this new technology represents a beacon of hope. By reducing the risks associated with current stent technologies, it could transform the landscape of cardiovascular treatment, paving the way for safer and more effective intervention strategies. Keep an eye on this developing story, as it may reshape your understanding of cardiovascular care in the near future!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)