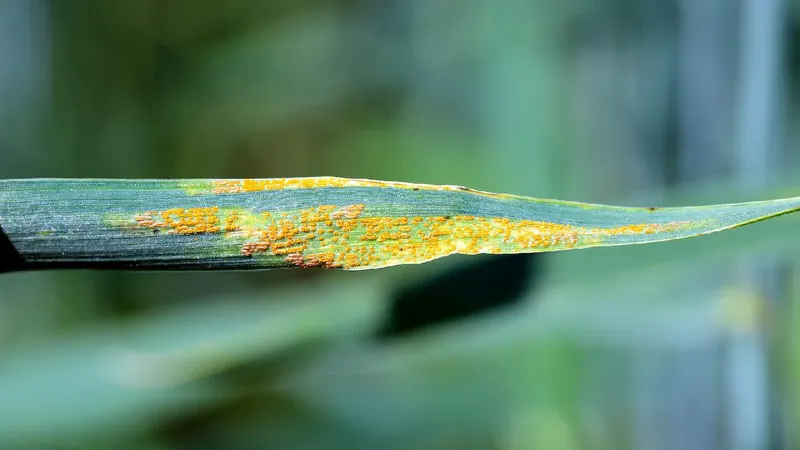

Breakthrough in Wheat Resistance: Scientists Unveil Genetic Map to Combat 'Wheat Cancer'
2025-07-25
Author: John Tan
A Game-Changer for Global Agriculture
In a groundbreaking development, Chinese scientists have created the world’s first genetic map pinpointing how wheat can resist the destructive yellow rust fungus – a disease so severe it’s often dubbed 'wheat cancer.' This innovation ushers in a new era of durable wheat varieties and could significantly reduce our reliance on pesticides.
Collaboration That Could Save the Crop
Published in *Nature Genetics*, this pioneering research was a collaborative effort between the Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University (NWAFU) and the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology under the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Thanks to their work, plant breeders now possess an unparalleled tool to navigate wheat's genetic landscape.
The Menace of Yellow Rust
Yellow rust, caused by the fungus *Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici* (Pst), is notorious for mutating rapidly, spawning new pathogen variants every five years. This relentless disease accounts for nearly 10% of global wheat yield loss each year, a staggering statistic highlighted by Kang Zhensheng, a leading professor at NWAFU's plant immunity department.
Revolutionizing Resistance Breeding
Kang emphasizes that breeding resistant wheat varieties is crucial for managing this threat effectively. "For the first time, our study provides a systematic look at the genomic signatures and epidemiological traits of wheat-Pst interactions throughout the last century, revealing the co-evolutionary dance between resistance mechanisms and pathogen races," he remarked.
Five Years of Research Yielding Results
After five years of intense research, the team analyzed variome data from 2,191 wheat accessions globally, alongside over 47,000 records of yellow rust responses across different environments and pathogen races. This extensive research led to the identification of 431 yellow rust resistance loci, ultimately constructing a comprehensive genome-wide map of these resistance genes.
Novel Genes Uncovered
Among their findings were 559 candidate genes linked to yellow rust resistance. Notably, they successfully cloned three innovative resistance genes. One standout, the novel allele Yr5x, showed remarkable resistance across multiple Pst races, showcasing the potential for genetic variation to enhance resistance.
Dual Defense Mechanisms Revealed
Additionally, Gene Yr6/Pm5 offers a dual line of defense against both yellow rust and powdery mildew (*Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici*), revealing a new strategy for comprehensive disease resistance. Another notable gene, YrKB (TaEDR2-B), provides extensive rust resistance without compromising yield.
A Major Leap for Sustainable Farming
The identification of these 'elite' haplotypes that merge resistance with high agricultural performance marks a significant stride in plant genetics, paving the way for a more sustainable approach to wheat farming and potentially transforming global food security.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)