Breakthrough in Turtle Health: Fast New Tests for Deadly Virus
2025-08-18
Author: Li
The Silent Threat: Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle Adenovirus Revealed
A new and perilous disease is wreaking havoc among farmed Chinese soft-shelled turtles in Jiangxi Province, China. Known for their culinary appeal, these turtles are suffering from significant egg production drops and severe internal bleeding, raising alarms among aquaculture specialists.
Meet CSTAdV: The New Virus on the Block
Scientists have provisionally named the newly identified virus Chinese soft-shelled turtle adenovirus 1 (CSTAdV-1). After genomic analysis, it was classified under the Siadenovirus genus. This virus varies in severity from subclinical infections to potentially lethal conditions, carrying the stark possibility of devastating the turtle farming industry.
Speed is Key: Why Rapid Detection Matters
With the increasing urgency to control this virus, swift and reliable diagnostic methods have become essential. Rapid onsite testing can help manage outbreaks effectively, making early detection crucial for preventing significant losses in aquaculture.
Introducing RAA: The Future of Virus Detection
Recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) technology promises to revolutionize virus diagnostics thanks to its ability to amplify DNA efficiently at warm temperatures (37–42°C) in just 30 minutes. Compared to traditional methods, RAA offers a variety of detection formats including real-time fluorescence and lateral flow tests.
Side-by-Side Showdown: RAA vs. qPCR
To validate this promising technology, researchers developed two assays: the real-time fluorescence RAA (RF-RAA) and a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay. While qPCR is well-established for quantifying pathogens, RAA's quick response makes it a fantastic candidate for speedy onsite testing.
Pathogen Profiling: Gathering the Evidence
Clinical samples from diseased turtles were analyzed to isolate CSTAdV-1 alongside other microbes. Initial findings pointed to ominous clinical signs in turtles, including skin necrosis and bleeding, creating urgency for a robust diagnostic solution.
Optimizing Detection: The Science Behind the Methods
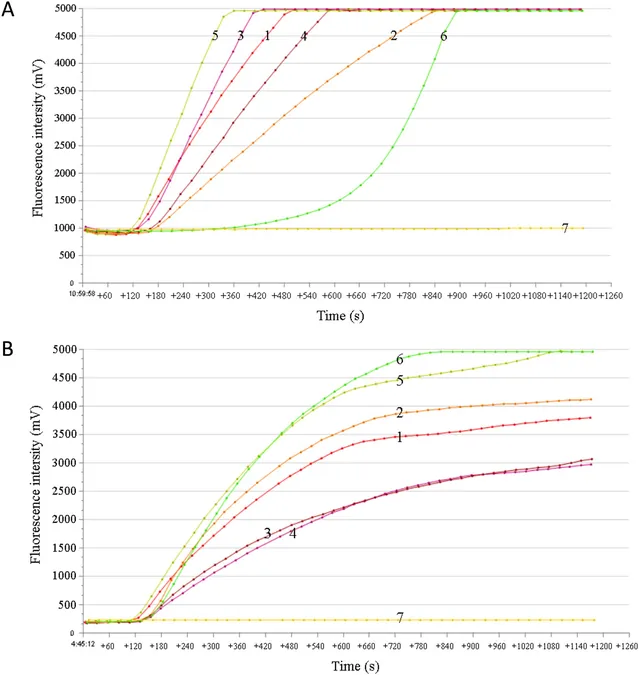
Research teams meticulously designed primers and probes, ensuring sensitivity and specificity for both RF-RAA and qPCR assays. The RF-RAA method demonstrated effective amplification, while qPCR underscored its reliability with a linear correlation for quantitative analysis.
Real-World Impact: Clinical Sample Testing
Both assays were put to the test with 107 archived DNA samples. The results were promising, with qPCR achieving a diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of 100%, while RF-RAA showcased a commendable 95.45% sensitivity.
Recommendations Going Forward: Combining Strengths
As researchers reflect on these findings, the consensus is clear. The qPCR technique is the gold standard for diagnostics in controlled laboratory settings due to its superior sensitivity. However, the RF-RAA technology holds significant potential for rapid, field-based testing.
Conclusion: A New Hope for Aquaculture
With the alarming rise of CSTAdV infections, these innovative diagnostic tools not only signify scientific progress but also offer a lifeline to the aquaculture industry. Early detection could mean the difference between life and death for many turtles, preserving both a delicacy and an economic asset.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)